A novel class of herpesvirus-encoded membrane-bound E3 ubiquitin ligases regulates endocytosis of proteins involved in immune recognition
- PMID: 11756476
- PMCID: PMC2199318
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200111010
A novel class of herpesvirus-encoded membrane-bound E3 ubiquitin ligases regulates endocytosis of proteins involved in immune recognition
Abstract
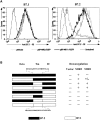
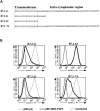
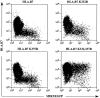
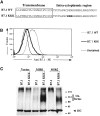
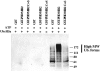
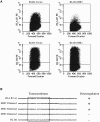
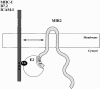
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encodes two transmembrane proteins (modulator of immune recognition [MIR]1 and MIR2) that downregulate cell surface molecules (MHC-I, B7.2, and ICAM-1) involved in the immune recognition of infected cells. This downregulation results from enhanced endocytosis and subsequent endolysosomal degradation of the target proteins. Here, we show that expression of MIR1 and MIR2 leads to ubiquitination of the cytosolic tail of their target proteins and that ubiquitination is essential for their removal from the cell surface. MIR1 and MIR2 both contain cytosolic zinc fingers of the PHD subfamily, and these structures are required for this activity. In vitro, addition of a MIR2-glutathione S-transferase (GST) fusion protein to purified E1 and E2 enzymes leads to transfer of ubiquitin (Ub) to GST-containing targets in an ATP- and E2-dependent fashion; this reaction is abolished by mutation of the Zn-coordinating residues of the PHD domain. Thus, MIR2 defines a novel class of membrane-bound E3 Ub ligases that modulates the trafficking of host cell membrane proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
c-MIR, a human E3 ubiquitin ligase, is a functional homolog of herpesvirus proteins MIR1 and MIR2 and has similar activity.J Biol Chem. 2003 Apr 25;278(17):14657-68. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211285200. Epub 2003 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12582153
-
Ubiquitination on nonlysine residues by a viral E3 ubiquitin ligase.Science. 2005 Jul 1;309(5731):127-30. doi: 10.1126/science.1110340. Science. 2005. PMID: 15994556
-
Functional organization of MIR2, a novel viral regulator of selective endocytosis.J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 22;277(8):6124-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110265200. Epub 2001 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11751860
-
A novel family of membrane-bound E3 ubiquitin ligases.J Biochem. 2006 Aug;140(2):147-54. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvj160. J Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16954532 Review.
-
What has the study of the K3 and K5 viral ubiquitin E3 ligases taught us about ubiquitin-mediated receptor regulation?Viruses. 2011 Feb;3(2):118-131. doi: 10.3390/v3020118. Epub 2011 Jan 28. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 22049306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitination by the membrane-associated RING-CH-8 (MARCH-8) ligase controls steady-state cell surface expression of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor 1.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 1;288(9):6617-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.448209. Epub 2013 Jan 8. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23300075 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Interactions with Adaptor-Protein Complexes: A Ubiquitous Trait among Viral Species.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 17;22(10):5274. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105274. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34067854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF54/dUTPase downregulates a ligand for the NK activating receptor NKp44.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(16):8693-704. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00252-12. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22674989 Free PMC article.
-
Requirements for the selective degradation of endoplasmic reticulum-resident major histocompatibility complex class I proteins by the viral immune evasion molecule mK3.J Virol. 2005 Apr;79(7):4099-108. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4099-4108.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15767411 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of gamma interferon receptor 1 by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K3 and K5.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(5):2117-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01961-06. Epub 2006 Dec 13. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17166914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boname, J.M., and P.G. Stevenson. 2001. Mhc class I ubiquitination by a viral phd/lap finger protein. Immunity. 15:627–636. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

