Synaptic potentials mediated by alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in supraoptic nucleus
- PMID: 11756485
- PMCID: PMC6757599
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-01-00029.2002
Synaptic potentials mediated by alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in supraoptic nucleus
Abstract
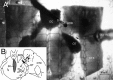
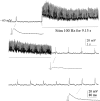
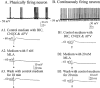
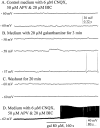
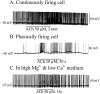
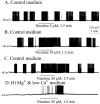
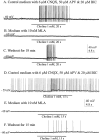
Brain slice preparations preserving projections from nearby forebrain cholinergic neurons to the supraoptic nucleus (SON) were used to study synaptic potentials mediated by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) in the hypothalamus. Paired-pulse electrical stimulation in an area anterior to the SON that was rich in cholinergic cells confirmed the monosynaptic nature of the connections to putative oxytocin and vasopressin SON neurons. With ionotropic glutamate and GABA(A) transmission blocked, this stimulation evoked fast, atropine-insensitive EPSPs that were sensitive to nAChR antagonists. Evoked EPSPs were blocked by methyllycaconitine and alpha-bungarotoxin, antagonists that are selective for nAChRs containing the alpha7 subunit, but not by dihydro-beta-erythroidine at concentrations known to antagonize alpha4beta2 nAChRs. Although anatomical evidence exists for postsynaptic alpha4beta2 nAChRs in the SON, these results indicate that postsynaptic alpha7 nAChRs are primarily responsible for the cholinergically mediated EPSPs. Repetitive stimulation suggested partial desensitization of the receptors. With ionotropic glutamate transmission blocked, inhibition of AChE increased spontaneous EPSP frequency and amplitude, suggesting spontaneous ACh release. ACh, nicotine, and choline (a selective alpha7 nAChR agonist) were effective in evoking action potentials and repetitive firing with synaptic transmission blocked by low Ca2+, high Mg2+ medium. These agonists were also effective in evoking the type of phasic bursts characteristic of vasopressin neurons, long thought to be completely dependent on activation of NMDA receptors (NMDARs). Because phasic bursting is Ca2+-dependent, the functional equivalence of alpha7 nAChR and NMDAR activation in this regard is likely attributable to their large Ca2+ fluxing capacities. This is the first demonstration that synaptically released ACh results in fast, alpha7 nAChR-mediated EPSPs in hypothalamic neurons.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synaptically released and exogenous ACh activates different nicotinic receptors to enhance evoked glutamatergic transmission in the lateral geniculate nucleus.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Oct;94(4):2549-60. doi: 10.1152/jn.00339.2005. Epub 2005 Jun 22. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15972832
-
Potentiation of glutamatergic synaptic input to supraoptic neurons by presynaptic nicotinic receptors.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001 Oct;281(4):R1105-13. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.2001.281.4.R1105. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11557616
-
Neuregulins increase alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and enhance excitatory synaptic transmission in GABAergic interneurons of the hippocampus.J Neurosci. 2001 Aug 1;21(15):5660-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05660.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11466437 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse strategies targeting α7 homomeric and α6β2* heteromeric nicotinic acetylcholine receptors for smoking cessation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014 Oct;1327(1):27-45. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12421. Epub 2014 Apr 14. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2014. PMID: 24730978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of neuroprotective effects of nicotine and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: role of alpha4 and alpha7 receptors in neuroprotection.J Mol Neurosci. 2010 Jan;40(1-2):211-6. doi: 10.1007/s12031-009-9236-1. J Mol Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 19714494 Review.
Cited by
-
Biphasic cholinergic synaptic transmission controls action potential activity in thalamic reticular nucleus neurons.J Neurosci. 2013 Jan 30;33(5):2048-59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3177-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23365242 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological regulation of magnocellular neurosecretory cell activity: integration of intrinsic, local and afferent mechanisms.J Neuroendocrinol. 2013 Aug;25(8):678-710. doi: 10.1111/jne.12051. J Neuroendocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23701531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel modulatory mechanisms revealed by the sustained application of nicotine in the guinea-pig hippocampus in vitro.J Physiol. 2003 Sep 1;551(Pt 2):539-50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.045492. Epub 2003 Jun 18. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12815181 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Regulation of Prelimbic and Thalamic Transmission to the Basolateral Amygdala by Acetylcholine Receptors.J Neurosci. 2023 Feb 1;43(5):722-735. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2545-21.2022. Epub 2022 Dec 19. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36535767 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible inhibition of GABAA receptors by alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors on the vertebrate postsynaptic neurons.J Physiol. 2007 Mar 15;579(Pt 3):753-63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.124578. Epub 2007 Jan 4. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17204496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque E. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons: I. Pharmacological and functional evidence for distinct structural subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:1455–1473. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Reriera E, Cortes W, Maelicke A, Albuquerque E. Choline is a selective agonist of alpha 7 nicotinic receptors in rat brain neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1997;9:2734–2742. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Pereira E, Albuquerque E. α-Bungarotoxin- and methllycaconitine-sensitive nicotinic receptors mediate fast synaptic transmission in interneurons of rat hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1998;810:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Bourque CW. Calcium-dependent spike after-current induces burst firing in magnocellular neurosecretory cells. Neurosci Lett. 1986;70:204–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
