Interaction between metabotropic and NMDA subtypes of glutamate receptors in sprout suppression at young synapses
- PMID: 11756506
- PMCID: PMC6757613
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-01-00226.2002
Interaction between metabotropic and NMDA subtypes of glutamate receptors in sprout suppression at young synapses
Abstract
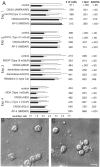
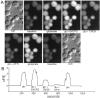
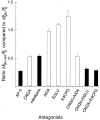
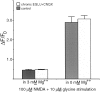
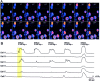
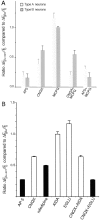
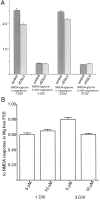
Recently, NMDA receptors (NMDARs) have been implicated in a cell contact-dependent suppression of sprouting in cultured Xenopus tectal neurons during an early period when neither AMPA/kainate (KA) receptors nor action potentials play a prominent role in cell-cell communication. We asked how the NMDA receptors function in the absence of the depolarizing effect of AMPA/KA receptor activity. We show that type II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) can operate synergistically with NMDA receptors in the absence of AMPA/KA receptor function to suppress an early neurite sprouting response of the tectal neurons. Calcium imaging with fluo-3 AM and morphological analyses after exposure to glutamate receptor antagonists show that a combination of AMPA/KA receptor and type II mGluR blockers mimics the decrease in intracellular free calcium in response to glutamate and the structural effects produced by NMDA receptor antagonists in these cultures. Patch-clamp analyses confirmed a decrease in NMDA receptor-mediated currents with type II mGluR blockade, and 8-bromo cAMP application produced a decrease in NMDA receptor-mediated calcium influx. These data suggest that type II mGluRs potentiate NMDA receptor function by decreasing cAMP levels in tectal neurons. We also show that NMDARs exhibit low magnesium sensitivity in tectal neurons during the first few days in culture. Thus both metabotropic and ionotropic glutamate receptors can play a role in the contact-mediated suppression of ongoing sprouting at early neuron-neuron contacts before action potential activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Suppression of sprouting: An early function of NMDA receptors in the absence of AMPA/kainate receptor activity.J Neurosci. 1998 May 15;18(10):3725-37. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-10-03725.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9570803 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium influx via ionotropic glutamate receptors causes long lasting inhibition of metabotropic glutamate receptor-coupled phosphoinositide hydrolysis.Neurochem Int. 1998 Sep;33(3):263-70. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(98)00030-8. Neurochem Int. 1998. PMID: 9759922
-
Role of Ca2+ stores in metabotropic L-glutamate receptor-mediated supralinear Ca2+ signaling in rat hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2000 Dec 1;20(23):8628-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-23-08628.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11102467 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental plasticity of NMDA receptors at the calyx of Held synapse.Neuropharmacology. 2021 Sep 15;196:108697. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108697. Epub 2021 Jul 6. Neuropharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34242682 Review.
-
Pharmacological and functional characterization of excitatory amino acid mediated cytotoxicity in cerebral cortical neurons.Cell Biol Toxicol. 1992 Jul-Sep;8(3):93-100. doi: 10.1007/BF00130515. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1992. PMID: 1332807 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel role of the nociceptin system as a regulator of glutamate transporter expression in developing astrocytes.Glia. 2017 Dec;65(12):2003-2023. doi: 10.1002/glia.23210. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Glia. 2017. PMID: 28906039 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Inactivation of the Serotonin Transporter Dysregulates Expression of Neurotransmission Genes and Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Levels in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex of Male Rats During Postnatal Development.Dev Neurobiol. 2025 Jul;85(3):e22973. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22973. Dev Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40485115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aniksztejn L, Bregestovski P, Ben-Ari Y. Selective activation of quisqualate metabotropic receptor potentiates NMDA but not AMPA responses. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991;205:327–328. - PubMed
-
- Beaver CJ, Ji Q, Daw NW. Effect of the group II metabotropic glutamate agonist, 2R,4R-APDC, varies with age, layer, and visual experience in the visual cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1999;82:86–93. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Developing networks play a similar melody. Trends Neurosci. 2001;24:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Burnashev N. Calcium permeability of ligand-gated channels. Cell Calcium. 1998;24:325–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
