A DNA damage-regulated BRCT-containing protein, TopBP1, is required for cell survival
- PMID: 11756551
- PMCID: PMC139754
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.2.555-566.2002
A DNA damage-regulated BRCT-containing protein, TopBP1, is required for cell survival
Abstract
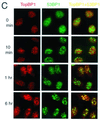
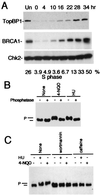
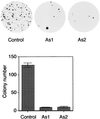
BRCA1 carboxyl-terminal (BRCT) motifs are present in a number of proteins involved in DNA repair and/or DNA damage-signaling pathways. Human DNA topoisomerase II binding protein 1 (TopBP1) contains eight BRCT motifs and shares sequence similarity with the fission yeast Rad4/Cut5 protein and the budding yeast DPB11 protein, both of which are required for DNA damage and/or replication checkpoint controls. We report here that TopBP1 is phosphorylated in response to DNA double-strand breaks and replication blocks. TopBP1 forms nuclear foci and localizes to the sites of DNA damage or the arrested replication forks. In response to DNA strand breaks, TopBP1 phosphorylation depends on the ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein (ATM) in vivo. However, ATM-dependent phosphorylation of TopBP1 does not appear to be required for focus formation following DNA damage. Instead, focus formation relies on one of the BRCT motifs, BRCT5, in TopBP1. Antisense Morpholino oligomers against TopBP1 greatly reduced TopBP1 expression in vivo. Similar to that of ataxia telangiectasia-related protein (ATR), Chk1, or Hus1, downregulation of TopBP1 leads to reduced cell survival, probably due to increased apoptosis. Taken together, the data presented here suggest that, like its putative counterparts in yeast species, TopBP1 may be involved in DNA damage and replication checkpoint controls.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Regulation of E2F1 by BRCT domain-containing protein TopBP1.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 May;23(9):3287-304. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.9.3287-3304.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12697828 Free PMC article.
-
Human TopBP1 ensures genome integrity during normal S phase.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(24):10907-15. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.10907-10915.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16314514 Free PMC article.
-
BRCT domain-containing protein TopBP1 functions in DNA replication and damage response.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 10;276(32):30399-406. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102245200. Epub 2001 Jun 6. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11395493
-
TopBP1 and DNA polymerase alpha-mediated recruitment of the 9-1-1 complex to stalled replication forks: implications for a replication restart-based mechanism for ATR checkpoint activation.Cell Cycle. 2009 Sep 15;8(18):2877-84. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.18.9485. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19652550 Review.
-
ATM signaling and 53BP1.Radiother Oncol. 2005 Aug;76(2):119-22. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2005.06.026. Radiother Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16024119 Review.
Cited by
-
Rif1 prevents resection of DNA breaks and promotes immunoglobulin class switching.Science. 2013 Feb 8;339(6120):711-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1230624. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Science. 2013. PMID: 23306439 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle-dependent inhibition of 53BP1 signaling by BRCA1.Cell Discov. 2015 Aug 4;1:15019. doi: 10.1038/celldisc.2015.19. eCollection 2015. Cell Discov. 2015. PMID: 27462418 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the DNA damage response on male meiotic sex chromosomes.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2105. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3105. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23812044 Free PMC article.
-
Xenopus Cut5 is essential for a CDK-dependent process in the initiation of DNA replication.EMBO J. 2003 May 15;22(10):2526-35. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg238. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12743046 Free PMC article.
-
A vertebrate gene, ticrr, is an essential checkpoint and replication regulator.Genes Dev. 2010 Jan 15;24(2):183-94. doi: 10.1101/gad.1860310. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20080954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banin, S., L. Moyal, S. Shieh, Y. Taya, C. W. Anderson, L. Chessa, N. I. Smorodinsky, C. Prives, Y. Reiss, Y. Shiloh, and Y. Ziv. 1998. Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science 281:1674–1677. - PubMed
-
- Blasina, A., I. V. de Weyer, M. C. Laus, W. H. Luyten, A. E. Parker, and C. H. McGowan. 1999. A human homologue of the checkpoint kinase Cds1 directly inhibits Cdc25 phosphatase. Curr. Biol. 9:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Blasina, A., B. D. Price, G. A. Turenne, and C. H. McGowan. 1999. Caffeine inhibits the checkpoint kinase ATM. Curr. Biol. 9:1135–1138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
