PAK5, a new brain-specific kinase, promotes neurite outgrowth in N1E-115 cells
- PMID: 11756552
- PMCID: PMC139731
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.2.567-577.2002
PAK5, a new brain-specific kinase, promotes neurite outgrowth in N1E-115 cells
Abstract
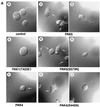
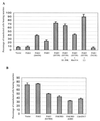
We have characterized a new member of the mammalian PAK family of serine/threonine kinases, PAK5, which is a novel target of the Rho GTPases Cdc42 and Rac. The kinase domain and GTPase-binding domain (GBD) of PAK5 are most closely related in sequence to those of mammalian PAK4. Outside of these domains, however, PAK5 is completely different in sequence from any known mammalian proteins. PAK5 does share considerable sequence homology with the Drosophila MBT protein (for "mushroom body tiny"), however, which is thought to play a role in development of cells in Drosophila brain. Interestingly, PAK5 is highly expressed in mammalian brain and is not expressed in most other tissues. We have found that PAK5, like Cdc42, promotes the induction of filopodia. In N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells, expression of PAK5 also triggered the induction of neurite-like processes, and a dominant-negative PAK5 mutant inhibited neurite outgrowth. Expression of activated PAK1 caused no noticeable changes in these cells. An activated mutant of PAK5 had an even more dramatic effect than wild-type PAK5, indicating that the morphologic changes induced by PAK5 are directly related to its kinase activity. Although PAK5 activates the JNK pathway, dominant-negative JNK did not inhibit neurite outgrowth. In contrast, the induction of neurites by PAK5 was abolished by expression of activated RhoA. Previous work has shown that Cdc42 and Rac promote neurite outgrowth by a pathway that is antagonistic to Rho. Our results suggest, therefore, that PAK5 operates downstream to Cdc42 and Rac and antagonizes Rho in the pathway, leading to neurite development.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Cloning and characterization of PAK5, a novel member of mammalian p21-activated kinase-II subfamily that is predominantly expressed in brain.Oncogene. 2002 May 30;21(24):3939-48. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205478. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12032833
-
Identification of an autoinhibitory domain of p21-activated protein kinase 5.J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 5;278(36):33621-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C300234200. Epub 2003 Jul 14. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12860998
-
p21-Activated kinase 5 (Pak5) localizes to mitochondria and inhibits apoptosis by phosphorylating BAD.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;23(16):5526-39. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.16.5526-5539.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12897128 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of phosphorylation pathways by p21 GTPases. The p21 Ras-related Rho subfamily and its role in phosphorylation signalling pathways.Eur J Biochem. 1996 Dec 1;242(2):171-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0171r.x. Eur J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8973630 Review.
-
The role of Rho GTPases and associated kinases in regulating neurite outgrowth.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;34(7):731-45. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(01)00167-4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11950591 Review.
Cited by
-
PAK signaling in oncogenesis.Oncogene. 2009 Jul 16;28(28):2545-55. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.119. Epub 2009 May 25. Oncogene. 2009. PMID: 19465939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAK4-6 in cancer and neuronal development.Cell Logist. 2012 Apr 1;2(2):95-104. doi: 10.4161/cl.21171. Cell Logist. 2012. PMID: 23125951 Free PMC article.
-
CDC42 binds PAK4 via an extended GTPase-effector interface.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jan 16;115(3):531-536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1717437115. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29295922 Free PMC article.
-
P21-activated kinase 7 mediates cisplatin-resistance of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells with Aurora-A overexpression.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 1;9(12):e113989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113989. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25436453 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of P21-activated kinase 5 protein is associated with poor survival in gastric cancer.Oncol Lett. 2017 Jul;14(1):404-410. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6115. Epub 2017 May 3. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28693183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagrodia, S., B. Derijard, R. J. Davis, and R. A. Cerione. 1995. Cdc42 and PAK-mediated signaling leads to Jun kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 270:27995–27998. - PubMed
-
- Berninger, B., and M. Poo. 1996. Fast actions of neurotrophic factors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 6:324–330. - PubMed
-
- Brown, J. L., L. Stowers, M. Baer, J. Trejo, S. Coughlin, and J. Chant. 1996. Human Ste20 homologue hPAK1 links GTPases to the JNK MAP kinase pathway. Curr. Biol. 6:598–605. - PubMed
-
- Brown, M. D., B. J. Cornejo, and J. R. Bamburg. 2000. Cdc42 stimulates neurite outgrowth and formation of growth cone filopodia and lamellipodia. J. Neurobiol 43:352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
