Transactivation of Fra-1 and consequent activation of AP-1 occur extracellular signal-regulated kinase dependently
- PMID: 11756554
- PMCID: PMC139745
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.2.587-598.2002
Transactivation of Fra-1 and consequent activation of AP-1 occur extracellular signal-regulated kinase dependently
Abstract
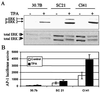
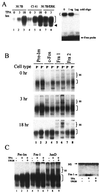
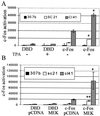
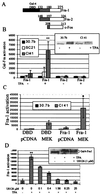
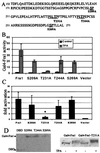
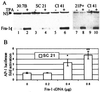
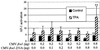
Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase, extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) play an important role in activating AP-1-dependent transcription. Studies using the JB6 mouse epidermal model and a transgenic mouse model have established a requirement for AP-1-dependent transcription in tumor promotion. Tumor promoters such as 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) and epidermal growth factor induce activator protein 1 (AP-1) activity and neoplastic transformation in JB6 transformation-sensitive (P(+)) cells, but not in transformation-resistant (P(-)) variants. The resistance in one of the P(-) variants can be attributed to the low levels of the MAP kinases, ERKs 1 and 2, and consequent nonresponsiveness to AP-1 activation. The resistant variant is not deficient in c-fos transcription. The purpose of these studies was to define the targets of activated ERK that lead to AP-1 transactivation. The results establish that the transactivation domain of Fra-1 can be activated, that activation of Fra-1 is ERK dependent, and that a putative ERK phosphorylation site must be intact for activation to occur. Fra-1 was activated by TPA in ERK-sufficient P(+) cells but not in ERK-deficient P(-) cells. A similar activation pattern was seen for c-Fos but not for Fra-2. Gel shift analysis identified Fra-1 as distinguishing mitogen-activated (P(+)) from nonactivated (P(-)) AP-1 complexes. A second AP-1-nonresponsive P(-) variant that underexpresses Fra-1 gained AP-1 response upon introduction of a Fra-1 expression construct. These observations suggest that ERK-dependent activation of Fra-1 is required for AP-1 transactivation in JB6 cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Expression of dominant negative Erk2 inhibits AP-1 transactivation and neoplastic transformation.Oncogene. 1998 Dec 31;17(26):3493-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202259. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 10030673
-
Dominant-negative c-Jun (TAM67) target genes: HMGA1 is required for tumor promoter-induced transformation.Oncogene. 2004 May 27;23(25):4466-76. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207581. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15064752
-
Shortage of mitogen-activated protein kinase is responsible for resistance to AP-1 transactivation and transformation in mouse JB6 cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jan 6;95(1):156-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.156. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9419345 Free PMC article.
-
Activator protein 1 (AP-1)- and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-dependent transcriptional events in carcinogenesis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2000 May 1;28(9):1338-48. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00220-3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000. PMID: 10924853 Review.
-
Gene regulation and genetic susceptibility to neoplastic transformation: AP-1 and p80 expression in JB6 cells.Environ Health Perspect. 1991 Jun;93:111-9. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9193111. Environ Health Perspect. 1991. PMID: 1773784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Old players with a newly defined function: Fra-1 and c-Fos support growth of human malignant breast tumors by activating membrane biogenesis at the cytoplasm.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053211. Epub 2013 Jan 2. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23301044 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of FRA1 (FOSL1) Leads to Global Transcriptional Perturbations, Reduced Cellular Adhesion and Altered Cell Cycle Progression.Cells. 2023 Sep 24;12(19):2344. doi: 10.3390/cells12192344. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830558 Free PMC article.
-
ERK2 but not ERK1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation via DEF motif-dependent signaling events.Mol Cell. 2010 Apr 9;38(1):114-27. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.02.020. Mol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20385094 Free PMC article.
-
Phorbol-12-myristate 13-acetate inhibits Nephronectin gene expression via Protein kinase C alpha and c-Jun/c-Fos transcription factors.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 13;11(1):20360. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00034-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34645824 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin-uPAR signaling leads to FRA-1 phosphorylation and enhanced breast cancer invasion.Breast Cancer Res. 2018 Jan 30;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13058-018-0936-8. Breast Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29382358 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abate, C., D. R. Marshak, and T. Curran. 1991. Fos is phosphorylated by p34cdc2, cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C at multiple sites clustered within regulatory regions. Oncogene 6:2179–2185. - PubMed
-
- Angel, P., and M. Karin. 1991. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1072:129–157. - PubMed
-
- Balmanno, K., and S. J. Cook. 1999. Sustained MAP kinase activation is required for the expression of cyclin D1, p21Cip1 and a subset of AP-1 proteins in CCL39 cells. Oncogene 18:3085–3097. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari, E. T., L. R. Bernstein, and N. H. Colburn. 1992. Differential c-jun expression in response to tumor promoters in JB6 cells sensitive or resistant to neoplastic transformation. Mol. Carcinog. 5:62–74. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
