AAA-ATPase p97/Cdc48p, a cytosolic chaperone required for endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation
- PMID: 11756557
- PMCID: PMC139744
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.2.626-634.2002
AAA-ATPase p97/Cdc48p, a cytosolic chaperone required for endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation
Abstract
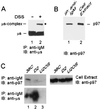
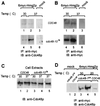
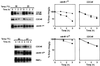
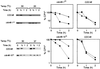
Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) disposes of aberrant proteins in the secretory pathway. Protein substrates of ERAD are dislocated via the Sec61p translocon from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol, where they are ubiquitinated and degraded by the proteasome. Since the Sec61p channel is also responsible for import of nascent proteins, this bidirectional passage should be coordinated, probably by molecular chaperones. Here we implicate the cytosolic chaperone AAA-ATPase p97/Cdc48p in ERAD. We show the association of mammalian p97 and its yeast homologue Cdc48p in complexes with two respective ERAD substrates, secretory immunoglobulin M in B lymphocytes and 6myc-Hmg2p in yeast. The membrane 6myc-Hmg2p as well as soluble lumenal CPY*, two short-lived ERAD substrates, are markedly stabilized in conditional cdc48 yeast mutants. The involvement of Cdc48p in dislocation is underscored by the accumulation of ERAD substrates in the endoplasmic reticulum when Cdc48p fails to function, as monitored by activation of the unfolded protein response. We propose that the role of p97/Cdc48p in ERAD, provided by its potential unfoldase activity and multiubiquitin binding capacity, is to act at the cytosolic face of the endoplasmic reticulum and to chaperone dislocation of ERAD substrates and present them to the proteasome.
Figures

References
-
- Amitay, R., S. Bar-Nun, J. Haimovich, E. Rabinovich, and I. Shachar. 1991. Post-translational regulation of IgM expression in B lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 266:12568–12573. - PubMed
-
- Amitay, R., I. Shachar, E. Rabinovich, J. Haimovich, and S. Bar-Nun. 1992. Degradation of secretory IgM in B lymphocytes occurs in a post-endoplasmic reticulum compartment and is mediated by a cysteine protease. J. Biol. Chem. 267:20694–20700. - PubMed
-
- Bays, N. W., R. G. Gardner, L. P. Seelig, C. A. Joazeiro, and R. Y. Hampton. 2001. Hrd1p/Der3p is a membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase required for ER-associated degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 3:24–29. - PubMed
-
- Biederer, T., C. Volkwein, and T. Sommer. 1997. Role of Cue1p in ubiquitination and degradation at the ER surface. Science 278:1806–1809. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
