Obligate roles for p16(Ink4a) and p19(Arf)-p53 in the suppression of murine pancreatic neoplasia
- PMID: 11756558
- PMCID: PMC139752
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.2.635-643.2002
Obligate roles for p16(Ink4a) and p19(Arf)-p53 in the suppression of murine pancreatic neoplasia
Abstract
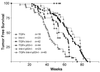
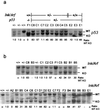
Epithelial tumors of the pancreas exhibit a wide spectrum of histologies with varying propensities for metastasis and tissue invasion. The histogenic relationship among these tumor types is not well established; moreover, the specific role of genetic lesions in the progression of these malignancies is largely undefined. Transgenic mice with ectopic expression of transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-alpha) in the pancreatic acinar cells develop tubular metaplasia, a potential premalignant lesion of the pancreatic ductal epithelium. To evaluate the cooperative interactions between TGF-alpha and signature mutations in pancreatic tumor genesis and progression, TGFalpha transgenic mice were crossed onto Ink4a/Arf and/or p53 mutant backgrounds. These compound mutant mice developed a novel pancreatic neoplasm, serous cystadenoma (SCA), presenting as large epithelial tumors bearing conspicuous gross and histological resemblances to their human counterpart. TGFalpha animals heterozygous for both the Ink4a/Arf and the p53 mutation showed a dramatically increased incidence of SCA, indicating synergistic interaction of these alleles. Inactivation of p16(Ink4a) by loss of heterozygosity, intragenic mutation, or promoter hypermethylation was a common feature in these SCAs, and correspondingly, none of the tumors expressed wild-type p16(Ink4a). All tumors sustained loss of p53 or Arf, generally in a mutually exclusive fashion. The tumor incidence data and molecular profiles establish a pathogenic role for the dual inactivation of p16(Ink4a) and p19(Arf)-p53 in the development of SCA in mice, demonstrating that p16(Ink4a) is a murine tumor suppressor. This genetically defined model provides insights into the molecular pathogenesis of SCA and serves as a platform for dissection of cell-specific programs of epithelial tumor suppression.
Figures


References
-
- Baba, M., S. Hirai, S. Kawakami, T. Kishida, N. Sakai, S. Kaneko, M. Yao, T. Shuin, Y. Kubota, M. Hosaka, and S. Ohno. 2001. Tumor suppressor protein VHL is induced at high cell density and mediates contact inhibition of cell growth. Oncogene 20:2727–2736. - PubMed
-
- Bockman, D. E., and G. Merlino. 1992. Cytological changes in the pancreas of transgenic mice overexpressing transforming growth factor alpha. Gastroenterology 103:1883–1892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
