Apoptosis in neural crest cells by functional loss of APC tumor suppressor gene
- PMID: 11756652
- PMCID: PMC117555
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.012264999
Apoptosis in neural crest cells by functional loss of APC tumor suppressor gene
Abstract
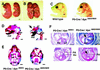
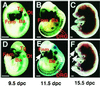
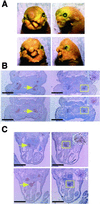
Apc is a gene associated with familial adenomatous polyposis coli (FAP) and its inactivation is a critical step in colorectal tumor formation. The protein product, adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), acts to down-regulate intracellular levels of beta-catenin, a key signal transducer in the Wnt signaling. Conditional targeting of Apc in the neural crest of mice caused massive apoptosis of cephalic and cardiac neural crest cells at about 11.5 days post coitum, resulting in craniofacial and cardiac anomalies at birth. Notably, the apoptotic cells localized in the regions where beta-catenin had accumulated. In contrast to its role in colorectal epithelial cells, inactivation of APC leads to dysregulation of beta-catenin/Wnt signaling with resultant apoptosis in certain tissues including neural crest cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The subcellular destinations of APC proteins.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002 May;3(5):328-38. doi: 10.1038/nrm806. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11988767 Review.
-
Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by the Wnt and ras pathways.Cancer Res. 2003 Feb 1;63(3):728-34. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12566320
-
[The role of APC in colonic cancerogenesis: zeroing in on Myc].Bull Cancer. 1998 Nov;85(11):925-8. Bull Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9951419 Review. French.
-
Cellular localization and signaling activity of beta-catenin in migrating neural crest cells.Dev Dyn. 2004 Aug;230(4):708-26. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20091. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 15254905
-
Novel colon cancer cell lines leading to better understanding of the diversity of respective primary cancers.Oncogene. 2002 Jul 11;21(30):4646-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205577. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12096341
Cited by
-
Cytoskeleton out of the cupboard: colon cancer and cytoskeletal changes induced by loss of APC.Nat Rev Cancer. 2006 Dec;6(12):967-74. doi: 10.1038/nrc2010. Epub 2006 Nov 9. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006. PMID: 17093505 Review.
-
Winding through the WNT pathway during cellular development and demise.Histol Histopathol. 2006 Jan;21(1):103-24. doi: 10.14670/HH-21.103. Histol Histopathol. 2006. PMID: 16267791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The activation of beta-catenin by Wnt signaling mediates the effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors.Exp Cell Res. 2007 May 1;313(8):1652-66. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.02.008. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17359971 Free PMC article.
-
Cranium growth, patterning and homeostasis.Development. 2022 Nov 15;149(22):dev201017. doi: 10.1242/dev.201017. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Development. 2022. PMID: 36408946 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothesis: Sam68 and Pygo2 mediate cell type-specific effects of the modulation of CBP-Wnt and p300-Wnt activities in Colorectal Cancer Cells.J Cancer. 2021 Jun 16;12(16):5046-5052. doi: 10.7150/jca.59726. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34234873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishisho I, Nakamura Y, Miyoshi Y, Miki Y, Ando H, Horii A, Koyama K, Utsunomiya J, Baba S, Hedge P. Science. 1991;253:665–669. - PubMed
-
- Joslyn G, Carlson M, Thliveris A, Albertsen H, Gelbert L, Samowitz W, Groden J, Stevens J, Spirio L, Robertson M, et al. Cell. 1991;66:601–613. - PubMed
-
- Miyoshi Y, Nagase H, Ando H, Horii A, Ichii S, Nakatsuru S, Aoki T, Miki Y, Mori T, Nakamura Y. Hum Mol Genet. 1992;1:229–233. - PubMed
-
- Shibata H, Toyama K, Shioya H, Ito M, Hirota M, Hasegawa S, Matsumoto H, Takano H, Akiyama T, Toyoshima K, et al. Science. 1997;278:120–123. - PubMed
-
- Polakis P. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1332:127–147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

