Adenovirus-mediated increase of HNF-3 levels stimulates expression of transthyretin and sonic hedgehog, which is associated with F9 cell differentiation toward the visceral endoderm lineage
- PMID: 11763995
- PMCID: PMC5964945
- DOI: 10.3727/000000001783992542
Adenovirus-mediated increase of HNF-3 levels stimulates expression of transthyretin and sonic hedgehog, which is associated with F9 cell differentiation toward the visceral endoderm lineage
Abstract
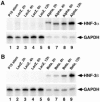
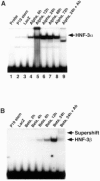
Retinoic acid-induced differentiation of mouse F9 embryonal carcinoma cells toward the visceral endoderm lineage is accompanied by increased expression of the Forkhead Box (Fox) transcription factors hepatocyte nuclear factor 3a (HNF-3alpha) and HNF-3beta, suggesting that they play a crucial role in visceral endoderm development. Retinoic acid stimulation results in a cascade of HNF-3 induction in which HNF-3alpha is a primary target for retinoic acid action and its increase is required for subsequent induction of HNF-3beta expression. Increased expression of HNF-3beta precedes activation of its known target genes, including transthyretin (TTR), Sonic hedgehog (Shh), HNF-1alpha, HNF-1beta, and HNF-4alpha. In order to examine whether increased HNF-3 expression is sufficient to induce expression of its downstream target genes without retinoic acid stimulation, we have used adenovirus-based expression vectors to increase HNF-3 protein levels in F9 cells. We demonstrate that adenovirus-mediated increase of HNF-3alpha levels in F9 cells is sufficient to induce activation of endogenous HNF-3beta levels followed by increased TTR and Shh expression. Furthermore, we show that elevated HNF-3beta levels stimulate expression of endogenous TTR and Shh without retinoic acid stimulation. Moreover, ectopic HNF-3 levels in undifferentiated F9 cells are insufficient to induce HNF-3alpha, HNF-1alpha, HNF-1beta, and HNF-4alpha expression, suggesting that their transcriptional activation required other regulatory proteins induced by the retinoic acid differentiation program. Finally, our studies demonstrate the utility of cell infections with adenovirus expressing distinct transcription factors to identify endogenous target genes, which are assembled with the appropriate nucleosome structure.
Figures




References
-
- Ang S. L.; Rossant J. HNF-3β is essential for node and notochord formation in mouse development. Cell 78:561–574; 1994. - PubMed
-
- Ang S. L.; Wierda A.; Wong D.; Stevens K. A.; Cascio S.; Rossant J.; Zaret K. S. The formation and maintenance of the definitive endoderm lineage in the mouse: Involvement of HNF3/forkhead proteins. Development 119:1301–1315; 1993. - PubMed
-
- Clark K. L.; Halay E. D.; Lai E.; Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature 364:412–420; 1993. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
