Integrin alphavbeta1 is a receptor for foot-and-mouth disease virus
- PMID: 11773368
- PMCID: PMC135819
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.3.935-941.2002
Integrin alphavbeta1 is a receptor for foot-and-mouth disease virus
Abstract
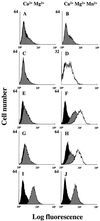
Infection by field strains of Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) is initiated by binding to certain species of arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD)-dependent integrin including alphavbeta3 and the epithelial integrin alphavbeta6. In this report we show that the integrin alphavbeta1, when expressed as a human/hamster heterodimer on transfected CHOB2 cells, is a receptor for FMDV. Virus binding and infection mediated by alphavbeta1 was inefficient in the presence of physiological concentrations of calcium and magnesium but were significantly enhanced by reagents that activate the integrin and promote ligand binding. The ability of chimeric alpha5/alphav integrin subunits, in association with the beta1 chain, to bind FMDV and mediate infection matched the ligand binding specificity of alphavbeta1, not alpha5beta1, thus providing further evidence for the receptor role of alphavbeta1. In addition, data are presented suggesting that amino acid residues near the RGD motif may be important for differentiating between the binding specificities of alphavbeta1 and alphavbeta6.
Figures
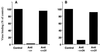

References
-
- Alexandersen, A., M. B. Oleksiewicz, and A. I. Donaldson. 2001. The early pathogenesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus in pigs infected by contact: a quantitative time-course study using TaqMan RT-PCR. J. Gen. Virol. 82:747–755. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni, G. N., D. Shih, C. A. Buck, and M. E. Hemler. 1995. Monoclonal antibody 9EG7 defines a novel β1 integrin epitope induced by soluble ligand and manganese, but inhibited by calcium. J. Biol. Chem. 270:25570–25577. - PubMed
-
- Bodary, S. C., and J. W. McLean. 1990. The integrin β1 subunit associates with the vitronectin receptor αv subunit to form a novel vitronectin receptor in a human embryonic kidney cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 265:5938–5941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

