Genetic, physical, and comparative map of the subtelomeric region of mouse Chromosome 4
- PMID: 11773963
- PMCID: PMC1994206
- DOI: 10.1007/s0033501-2109-8
Genetic, physical, and comparative map of the subtelomeric region of mouse Chromosome 4
Abstract
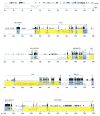
The subtelomeric region of mouse chromosome (Chr) 4 harbors loci with effects on behavior, development, and disease susceptibility. Regions near the telomeres are more difficult to map and characterize than other areas because of the unique features of subtelomeric DNA. As a result of these problems, the available mapping information for this part of mouse Chr 4 was insufficient to pursue candidate gene evaluation. Therefore, we sought to characterize the area in greater detail by creating a comprehensive genetic, physical, and comparative map. We constructed a genetic map that contained 30 markers and covered 13.3 cM; then we created a 1.2-Mb sequence-ready BAC contig, representing a 5.1-cM area, and sequenced a 246-kb mouse BAC from this contig. The resulting sequence, as well as approximately 40 kb of previously deposited genomic sequence, yielded a total of 284 kb of sequence, which contained over 20 putative genes. These putative genes were confirmed by matching ESTs or cDNA in the public databases to the genomic sequence and/or by direct sequencing of cDNA. Comparative genome sequence analysis demonstrated conserved synteny between the mouse and the human genomes (1p36.3). DNA from two strains of mice (C57BL/6ByJ and 129P3/J) was sequenced to detect single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The frequency of SNPs in this region was more than threefold higher than the genome-wide average for comparable mouse strains (129/Sv and C57BL/6J). The resulting SNP map, in conjunction with the sequence annotation and with physical and genetic maps, provides a detailed description of this gene-rich region. These data will facilitate genetic and comparative mapping studies and identification of a large number of novel candidate genes for the trait loci mapped to this region.
Figures




References
-
- Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, Plomin R, McClearn GE, Sampson KE, et al. Single-locus control of saccharin intake in BXD/Ty recombinant inbred (RI) mice: some methodological implications for RI strain analysis. Behav Genet. 1992;22:81–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

