A genomewide linkage screen for relative hand skill in sibling pairs
- PMID: 11774074
- PMCID: PMC384959
- DOI: 10.1086/339249
A genomewide linkage screen for relative hand skill in sibling pairs
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet 2002 Apr;70(4):1075
Abstract
Genomewide quantitative-trait locus (QTL) linkage analysis was performed using a continuous measure of relative hand skill (PegQ) in a sample of 195 reading-disabled sibling pairs from the United Kingdom. This was the first genomewide screen for any measure related to handedness. The mean PegQ in the sample was equivalent to that of normative data, and PegQ was not correlated with tests of reading ability (correlations between minus sign0.13 and 0.05). Relative hand skill could therefore be considered normal within the sample. A QTL on chromosome 2p11.2-12 yielded strong evidence for linkage to PegQ (empirical P=.00007), and another suggestive QTL on 17p11-q23 was also identified (empirical P=.002). The 2p11.2-12 locus was further analyzed in an independent sample of 143 reading-disabled sibling pairs, and this analysis yielded an empirical P=.13. Relative hand skill therefore is probably a complex multifactorial phenotype with a heterogeneous background, but nevertheless is amenable to QTL-based gene-mapping approaches.
Figures

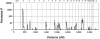
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Cooperative Human Linkage Center, The, http://lpg.nci.nih.gov/ABI/ (for ABI PRISM Reference Maps)
-
- Documentation to the SIMULATE Program, http://linkage.rockefeller.edu/ott/simulate.htm
-
- Kruglyak Lab Home Page, http://www.fhcrc.org/labs/kruglyak/Downloads/ (for GENEHUNTER 2.0)
-
- MAPMAKER/SIBS, http://www-genome.wi.mit.edu/ftp/distribution/software/sibs/
References
-
- Annett M (1985) Left, right, hand and brain: the right shift theory. Laurence Erlbaum, London
-
- ——— (1994) Handedness as a continuous variable with dextral shift: sex, generation, and family handedness in subgroups of left- and right-handers. Behav Genet 24:51–63 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

