Micro-RNAs: small is plentiful
- PMID: 11781331
- PMCID: PMC2173595
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200111033
Micro-RNAs: small is plentiful
Abstract
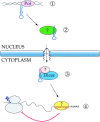
Two small temporally regulated RNAs (stRNAs)* of approximately 22 nucleotides regulate timing of gene expression during development of the nematode C. elegans. This regulation occurs at a posttranscriptional, presumably translational, level and is distinct from RNA interference (RNAi). One of the two stRNAs, let-7, as well as its target gene, lin-41, are highly conserved even in humans, suggesting a wide employment of stRNA-mediated gene regulation. Recent reports indicate that these two stRNAs are indeed likely to represent only the tip of an iceberg with hundreds or more of additional micro-RNAs (miRNAs) existing in metazoans. miRNAs might thus be previously underestimated key participants in the field of gene regulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of developmental timing by small temporal RNAs: a paradigm for RNA-mediated regulation of gene expression.Bioessays. 2002 Feb;24(2):119-29. doi: 10.1002/bies.10046. Bioessays. 2002. PMID: 11835276 Review.
-
An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans.Science. 2001 Oct 26;294(5543):858-62. doi: 10.1126/science.1065062. Science. 2001. PMID: 11679671
-
Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs.Science. 2001 Oct 26;294(5543):853-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1064921. Science. 2001. PMID: 11679670
-
Translational control of endogenous microRNA target genes in C. elegans.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2010;50:21-40. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-03103-8_2. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19841879 Review.
-
The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans.Genes Dev. 2003 Apr 15;17(8):991-1008. doi: 10.1101/gad.1074403. Epub 2003 Apr 2. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12672692 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Analysis of the Chicken Follicular Theca Cells with miR-135a-5p Suppressed.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 Nov 5;10(11):4071-4081. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401701. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32900904 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary connection between the catalytic subunits of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases and eukaryotic RNA-dependent RNA polymerases and the origin of RNA polymerases.BMC Struct Biol. 2003 Jan 28;3:1. doi: 10.1186/1472-6807-3-1. Epub 2003 Jan 28. BMC Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12553882 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal and spatial patterning of an organ by a single transcription factor.Genome Biol. 2005;6(2):205. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-2-205. Epub 2005 Jan 25. Genome Biol. 2005. PMID: 15693952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA expression profile in intrauterine hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypoplasia in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Sep;8(3):747-753. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1796. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 25120593 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous and silencing-associated small RNAs in plants.Plant Cell. 2002 Jul;14(7):1605-19. doi: 10.1105/tpc.003210. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 12119378 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banerjee, D., and F. Slack. 2002. Control of developmental timing by small temporal RNAs: a paradigm for RNA-mediated regulation of gene expression. Bioessays. In press. - PubMed
-
- Chalfie, M., H.R. Horvitz, and J.E. Sulston. 1981. Mutations that lead to reiterations in the cell lineages of C. elegans. Cell. 24:59–69. - PubMed
-
- Elbashir, S.M., J. Harborth, W. Lendeckel, A. Yalcin, K. Weber, and T. Tuschl. 2001. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 411:494–498. - PubMed
-
- Feinbaum, R., and V. Ambros. 1999. The timing of lin-4 RNA accumulation controls the timing of postembryonic developmental events in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev. Biol. 210:87–95. - PubMed
-
- Grishok, A., A.E. Pasquinelli, D. Conte, N. Li, S. Parrish, I. Ha, D.L. Baillie, A. Fire, G. Ruvkun, and C.C. Mello. 2001. Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans developmental timing. Cell. 106:23–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

