Characterization of Cep135, a novel coiled-coil centrosomal protein involved in microtubule organization in mammalian cells
- PMID: 11781336
- PMCID: PMC2173569
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200108088
Characterization of Cep135, a novel coiled-coil centrosomal protein involved in microtubule organization in mammalian cells
Abstract
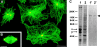
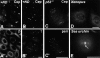
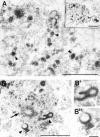
By using monoclonal antibodies raised against isolated clam centrosomes, we have identified a novel 135-kD centrosomal protein (Cep135), present in a wide range of organisms. Cep135 is located at the centrosome throughout the cell cycle, and localization is independent of the microtubule network. It distributes throughout the centrosomal area in association with the electron-dense material surrounding centrioles. Sequence analysis of cDNA isolated from CHO cells predicted a protein of 1,145-amino acid residues with extensive alpha-helical domains. Expression of a series of deletion constructs revealed the presence of three independent centrosome-targeting domains. Overexpression of Cep135 resulted in the accumulation of unique whorl-like particles in both the centrosome and the cytoplasm. Although their size, shape, and number varied according to the level of protein expression, these whorls were composed of parallel dense lines arranged in a 6-nm space. Altered levels of Cep135 by protein overexpression and/or suppression of endogenous Cep135 by RNA interference caused disorganization of interphase and mitotic spindle microtubules. Thus, Cep135 may play an important role in the centrosomal function of organizing microtubules in mammalian cells.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Interaction of Cep135 with a p50 dynactin subunit in mammalian centrosomes.Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2004 May;58(1):53-66. doi: 10.1002/cm.10175. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2004. PMID: 14983524
-
Filamentous polymers induced by overexpression of a novel centrosomal protein, Cep135.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Jun 1;49(5):478-86. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(20000601)49:5<478::AID-JEMT10>3.0.CO;2-J. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10842375
-
Centrosomal components immunologically related to tektins from ciliary and flagellar microtubules.J Cell Sci. 1994 Aug;107 ( Pt 8):2095-105. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.8.2095. J Cell Sci. 1994. PMID: 7983171
-
Role of centrosomal adaptor proteins of the TACC family in the regulation of microtubule dynamics during mitotic cell division.Biol Chem. 2013 Nov;394(11):1411-23. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0184. Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23787465 Review.
-
The Dictyostelium Centrosome.Cells. 2021 Oct 5;10(10):2657. doi: 10.3390/cells10102657. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685637 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential mechanisms of Zika-linked microcephaly.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2017 Jul;6(4):e273. doi: 10.1002/wdev.273. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28383800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Building a ninefold symmetrical barrel: structural dissections of centriole assembly.Open Biol. 2015 Aug;5(8):150082. doi: 10.1098/rsob.150082. Open Biol. 2015. PMID: 26269428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A truncating mutation of CEP135 causes primary microcephaly and disturbed centrosomal function.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 May 4;90(5):871-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.016. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22521416 Free PMC article.
-
Human microcephaly protein CEP135 binds to hSAS-6 and CPAP, and is required for centriole assembly.EMBO J. 2013 Apr 17;32(8):1141-54. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.56. Epub 2013 Mar 19. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23511974 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetics of human primary microcephaly: an overview.BMC Med Genomics. 2015;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S4. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-8-S1-S4. Epub 2015 Jan 15. BMC Med Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25951892 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersen, S.S. 1999. Molecular characteristics of the centrosome. Int. Rev. Cytol. 187:51–109. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, S.J., and M. Stewart. 1991. Expression in Escherichia coli of fragments of the coiled-coil rod domain of rabbit myosin: influence of different regions of the molecule on aggregation and paracrystal formation. J. Cell Sci. 99:823–836. - PubMed
-
- Bornens, M. 1977. Is the centriole bound to the nuclear membrane? Nature. 270:80–82. - PubMed
-
- Buendia, B., C. Antony, F. Verde, M. Bornens, and E. Karsenti. 1990. A centrosomal antigen localized on intermediate filaments and mitotic spindle poles. J. Cell Sci. 97:259–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

