Association of BAFF/BLyS overexpression and altered B cell differentiation with Sjögren's syndrome
- PMID: 11781351
- PMCID: PMC150825
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI14121
Association of BAFF/BLyS overexpression and altered B cell differentiation with Sjögren's syndrome
Abstract
BAFF (BLyS, TALL-1, THANK, zTNF4) is a member of the TNF superfamily that specifically regulates B lymphocyte proliferation and survival. Mice transgenic (Tg) for BAFF develop an autoimmune condition similar to systemic lupus erythematosus. We now demonstrate that BAFF Tg mice, as they age, develop a secondary pathology reminiscent of Sjögren's syndrome (SS), which is manifested by severe sialadenitis, decreased saliva production, and destruction of submaxillary glands. In humans, SS also correlates with elevated levels of circulating BAFF, as well as a dramatic upregulation of BAFF expression in inflamed salivary glands. A likely explanation for disease in BAFF Tg mice is excessive survival signals to autoreactive B cells, possibly as they pass through a critical tolerance checkpoint while maturing in the spleen. The marginal zone (MZ) B cell compartment, one of the enlarged B cell subsets in the spleen of BAFF Tg mice, is a potential reservoir of autoreactive B cells. Interestingly, B cells with an MZ-like phenotype infiltrate the salivary glands of BAFF Tg mice, suggesting that cells of this compartment potentially participate in tissue damage in SS and possibly other autoimmune diseases. We conclude that altered B cell differentiation and tolerance induced by excess BAFF may be central to SS pathogenesis.
Figures
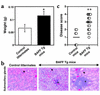
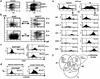
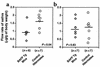
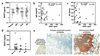
Comment in
-
The buzz about BAFF.J Clin Invest. 2002 Jan;109(1):17-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI14780. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 11781346 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jonsson, R., Haga, H.-J., and Gordon, T.P. 2000. Sjögren’s syndrome. In Arthritis and allied conditions. W. Koopman, editor. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. 1736–1759.
-
- Manoussakis, M.N., Talal, N., and Moutsopoulos, H.M. 1998. Sjögren’s syndrome. In The autoimmune diseases. N.R. Rose and I.R. Mackay, editors. Academic Press. San Diego, California, USA. 381–404.
-
- Haneji N, et al. Identification of α-fodrin as a candidate autoantigen in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Science. 1997; 276:604–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

