Rapid acquisition of tissue-specific homing phenotypes by CD4(+) T cells activated in cutaneous or mucosal lymphoid tissues
- PMID: 11781372
- PMCID: PMC2196018
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20011502
Rapid acquisition of tissue-specific homing phenotypes by CD4(+) T cells activated in cutaneous or mucosal lymphoid tissues
Abstract
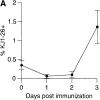
Effector and memory T cells can be subdivided based on their ability to traffic through peripheral tissues such as inflamed skin and intestinal lamina propria, a property controlled by expression of 'tissue-specific' adhesion and chemoattractant receptors. However, little is known about the development of these selectively homing T cell subsets, and it is unclear whether activation in cutaneous versus intestinal lymphoid organs directly results in effector/memory T cells that differentially express adhesion and chemoattractant receptors targeting them to the corresponding nonlymphoid site. We define two murine CD4(+) effector/memory T cell subsets that preferentially localize in cutaneous or intestinal lymphoid organs by their reciprocal expression of the adhesion molecules P-selectin ligand (P-lig) and alpha 4 beta 7, respectively. We show that within 2 d of systemic immunization CD4(+) T cells activated in cutaneous lymph nodes upregulate P-lig, and downregulate alpha 4 beta 7, while those responding to antigen in intestinal lymph nodes selectively express high levels of alpha 4 beta 7 and acquire responsiveness to the intestinal chemokine thymus-expressed chemokine (TECK). Thus, during an immune response, local microenvironments within cutaneous and intestinal secondary lymphoid organs differentially direct T cell expression of these adhesion and chemoattractant receptors, targeting the resulting effector T cells to the inflamed skin or intestinal lamina propria.
Figures







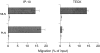
References
-
- Butcher, E.C., and L.J. Picker. 1996. Lymphocyte homing and homeostasis. Science. 272:60–66. - PubMed
-
- Butcher, E.C., M. Williams, K. Youngman, L. Rott, and M. Briskin. 1999. Lymphocyte trafficking and regional immunity. Adv. Immunol. 72:209–253. - PubMed
-
- Rott, L.S., M.J. Briskin, D.P. Andrew, E.L. Berg, and E.C. Butcher. 1996. A fundamental subdivision of circulating lymphocytes defined by adhesion to mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1. Comparison with vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and correlation with β7 integrins and memory differentiation. J. Immunol. 156:3727–3736. - PubMed
-
- Bargatze, R.F., M.A. Jutila, and E.C. Butcher. 1995. Distinct roles of L-selectin and integrins α4β7 and LFA-1 in lymphocyte homing to Peyer's patch-HEV in situ: the multistep model confirmed and refined. Immunity. 3:99–108. - PubMed
-
- Zabel, B.A., W.W. Agace, J.J. Campbell, H.M. Heath, D. Parent, A.I. Roberts, E.C. Ebert, N. Kassam, S. Qin, M. Zovko, et al. 1999. Human G protein-coupled receptor GPR-9-6/CC chemokine receptor 9 is selectively expressed on intestinal homing T lymphocytes, mucosal lymphocytes, and thymocytes and is required for thymus-expressed chemokine-mediated chemotaxis. J. Exp. Med. 190:1241–1256. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

