C/EBPalpha induces adipogenesis through PPARgamma: a unified pathway
- PMID: 11782441
- PMCID: PMC155311
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.948702
C/EBPalpha induces adipogenesis through PPARgamma: a unified pathway
Abstract
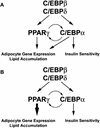
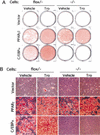
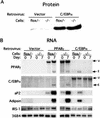
PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha are critical transcription factors in adipogenesis, but the precise role of these proteins has been difficult to ascertain because they positively regulate each other's expression. Questions remain about whether these factors operate independently in separate, parallel pathways of differentiation, or whether a single pathway exists. PPARgamma can promote adipogenesis in C/EBPalpha-deficient cells, but the converse has not been tested. We have created an immortalized line of fibroblasts lacking PPARgamma, which we use to show that C/EBPalpha has no ability to promote adipogenesis in the absence of PPARgamma. These results indicate that C/EBPalpha and PPARgamma participate in a single pathway of fat cell development with PPARgamma being the proximal effector of adipogenesis.
Figures

Comment in
-
Becoming fat.Genes Dev. 2002 Jan 1;16(1):1-5. doi: 10.1101/gad.964002. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 11782439 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barak Y, Nelson MC, Ong ES, Jones YZ, Ruiz-Lozano P, Chien KR, Koder A, Evans RM. PPAR gamma is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell. 1999;4:585–595. - PubMed
-
- Cao Z, Umek RM, McKnight SL. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes & Dev. 1991;5:1538–1552. - PubMed
-
- Dani C, Smith AG, Dessolin S, Leroy P, Staccini L, Villageois P, Darimont C, Ailhaud G. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells into adipocytes in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:1279–1285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
