Expression of mRNA and functional alpha(1)-adrenoceptors that suppress the GIRK conductance in adult rat locus coeruleus neurons
- PMID: 11786498
- PMCID: PMC1573116
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704453
Expression of mRNA and functional alpha(1)-adrenoceptors that suppress the GIRK conductance in adult rat locus coeruleus neurons
Abstract
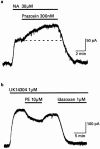
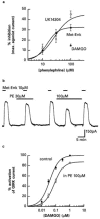
1. Locus coeruleus neurons in adult rats express binding sites and mRNA for alpha(1)-adrenoceptors even though the depolarizing effect of alpha(1)-adrenoceptor agonists on neonatal neurons disappears during development. 2. In this study intracellular microelectrodes were used to record from locus coeruleus neurons in brain slices of adult rats and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT - PCR) was used to investigate the mRNA expression of alpha(1)- and alpha(2)-adrenoceptors in juvenile and adult rats. 3. The alpha(1)-adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine had no effect on the membrane conductance of locus coeruleus neurons (V(hold) -60 mV) but decreased the G protein coupled, inward rectifier potassium (GIRK) conductance induced by alpha(2)-adrenoceptor or mu-opioid agonists. The GIRK conductance induced by noradrenaline was increased in amplitude when alpha(1)-adrenoceptors were blocked with prazosin. 4. RT - PCR of total cellular RNA isolated from microdissected locus coeruleus tissue demonstrated strong mRNA expression of alpha(1a)-, alpha(1b)- and alpha(1d)-adrenoceptors in both juvenile and adult rats. However, only mRNA transcripts for the alpha(1b)-adrenoceptors were consistently detected in cytoplasmic samples taken from single locus coeruleus neurons of juvenile rats, suggesting that this subtype may be responsible for the physiological effects seen in juvenile rats. 5. Juvenile and adult locus coeruleus tissue expressed mRNA for the alpha(2a)- and alpha(2c)-adrenoceptors while the alpha(2b)-adrenoceptor was only weakly expressed in juveniles and was not detected in adults. 6. The results of this study show that alpha(1)-adrenoceptors expressed in adult locus coeruleus neurons function to suppress the GIRK conductance that is activated by mu-opioid and alpha(2)-adrenoceptors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of the postjunctional alpha 2C-adrenoceptor mediating vasoconstriction to UK14304 in porcine pulmonary veins.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 May;151(2):186-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707221. Epub 2007 Mar 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17375080 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha1-adrenoceptors in the rat cerebral cortex: new insights into the characterization of alpha1L- and alpha1D-adrenoceptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Sep 1;641(1):41-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.05.016. Epub 2010 May 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20511116
-
Heterogeneous expression of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes among rat nephron segments.Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;44(5):926-33. Mol Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8246915
-
Alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes.Pharmacol Res. 2001 Sep;44(3):195-208. doi: 10.1006/phrs.2001.0857. Pharmacol Res. 2001. PMID: 11529686 Review.
-
Mechanisms of opioid actions on neurons of the locus coeruleus.Prog Brain Res. 1991;88:197-205. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63809-1. Prog Brain Res. 1991. PMID: 1667545 Review.
Cited by
-
μ-Opioid receptor activation and noradrenaline transport inhibition by tapentadol in rat single locus coeruleus neurons.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(2):460-8. doi: 10.1111/bph.12566. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24372103 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of functional μ opioid receptor turnover in rat locus coeruleus: an electrophysiological and immunocytochemical study.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Aug;174(16):2758-2772. doi: 10.1111/bph.13901. Epub 2017 Jul 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28589556 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic modulation of NPY/AgRP and POMC neurons in the arcuate nucleus by noradrenalin.Elife. 2017 Jun 20;6:e25770. doi: 10.7554/eLife.25770. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28632132 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological properties of catecholaminergic neurons in the norepinephrine-deficient mouse.Neuroscience. 2007 Feb 9;144(3):1067-74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.10.032. Epub 2006 Dec 6. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17156935 Free PMC article.
-
Rate-dependent behavioral effects of stimulation of central motoric alpha(1)-adrenoceptors: hypothesized relation to depolarization blockade.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005 Mar;178(2-3):109-14. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-2125-y. Epub 2005 Jan 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2005. PMID: 15645218 Review.
References
-
- CHAMBA G., WEISSMANN D., ROUSSET C., RENAUD B., PUJOL J.F. Distribution of alpha-1 and alpha-2 binding sites in the rat locus coeruleus. Brain Res. Bull. 1991;26:185–193. - PubMed
-
- CHRISTIE M.J., WILLIAMS J.T., NORTH R.A. Cellular mechanisms of opioid tolerance: studies in single brain neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 1987;32:633–638. - PubMed
-
- DAY H.E., CAMPEAU S., WATSON S.J., AKIL H. Distribution of alpha 1a-, alpha 1b- and alpha 1d-adrenergic receptor mRNA in the rat brain and spinal cord. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1997;13:115–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

