Three proliferating cell nuclear antigen-like proteins found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Aeropyrum pernix: interactions with the two DNA polymerases
- PMID: 11790738
- PMCID: PMC139509
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.184.3.687-694.2002
Three proliferating cell nuclear antigen-like proteins found in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Aeropyrum pernix: interactions with the two DNA polymerases
Abstract
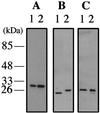
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is an essential component in the eukaryotic DNA replication machinery, in which it works for tethering DNA polymerases on the DNA template to accomplish processive DNA synthesis. The PCNA also interacts with many other proteins in important cellular processes, including cell cycle control, DNA repair, and an apoptotic pathway in the domain EUCARYA: We identified three genes encoding PCNA-like sequences in the genome of Aeropyrum pernix, a crenarchaeal archaeon. We cloned and expressed these genes in Escherichia coli and analyzed the gene products. All three PCNA homologs stimulated the primer extension activities of the two DNA polymerases, polymerase I (Pol I) and Pol II, identified in A. pernix to various extents, among which A. pernix PCNA 3 (ApePCNA3) provided a most remarkable effect on both Pol I and Pol II. The three proteins were confirmed to exist in the A. pernix cells. These results suggest that the three PCNAs work as the processivity factor of DNA polymerases in A. pernix cells under different conditions. In Eucarya, three checkpoint proteins, Hus1, Rad1, and Rad9, have been proposed to form a PCNA-like ring structure and may work as a sliding clamp for the translesion DNA polymerases. Therefore, it is very interesting that three active PCNAs were found in one archaeal cell. Further analyses are necessary to determine whether each PCNA has specific roles, and moreover, how they reveal different functions in the cells.
Figures
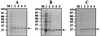
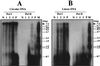
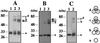

References
-
- Bocquier, A. A., L. Liu, I. K. O. Cann, K. Komori, D. Kohda, and Y. Ishino. 2001. Archaeal primase: bridging the gap between RNA and DNA polymerase. Curr. Biol. 11:452–456. - PubMed
-
- Cai, R. L., Y. Yan-Neale, M. A. Cueto, H. Xu, and D. Cohen. 2000. HDAC1, a histone deacetylase, forms a complex with Hus1 and Rad9, two G2/M checkpoint Rad proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 275:27909–27916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

