Ca(2+) regulation in guinea-pig colonic smooth muscle: the role of the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger and the sarcoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 11790813
- PMCID: PMC2290079
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013039
Ca(2+) regulation in guinea-pig colonic smooth muscle: the role of the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger and the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
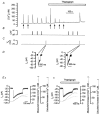
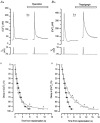
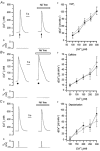
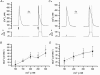
To study the contribution of the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger to Ca(2+) regulation and its interaction with the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), changes in cytoplasmic Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](c)) were measured in single, voltage clamped, smooth muscle cells. Increases in [Ca(2+)](c) were evoked by either depolarisation (-70 mV to 0 mV) or by release from the SR by caffeine (10 mM) or flash photolysis of caged InsP(3) (InsP(3)). Depletion of the SR of Ca(2+) (verified by the absence of a response to caffeine and InsP(3)) by either ryanodine (50 microM), to open the ryanodine receptors (RyRs), or thapsigargin (500 nM) or cyclopiazonic acid (CPA, 10 microM), to inhibit the SR Ca(2+) pumps, reduced neither the magnitude of the Ca(2+) transient nor the relationship between the influx of and the rise in [Ca(2+)](c) evoked by depolarisation. This suggested that Ca(2+)-induced Ca(2+) release (CICR) from the SR did not contribute significantly to the depolarisation-evoked rise in [Ca(2+)](c). However, although Ca(2+) was not released from it, the SR accumulated the ion following depolarisation since ryanodine and thapsigargin each slowed the rate of decline of the depolarisation-evoked Ca(2+) transient. Indeed, the SR Ca(2+) content increased following depolarisation as assessed by the increased magnitude of the [Ca(2+)](c) levels evoked each by InsP(3) and caffeine, relative to controls. The increased SR Ca(2+) content following depolarisation returned to control values in approximately 12 min via Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger activity. Thus inhibition of the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger by removal of external Na(+) (by either lithium or choline substitution) prevented the increased SR Ca(2+) content from returning to control levels. On the other hand, the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger did not appear to regulate bulk average Ca(2+) directly since the rates of decline in [Ca(2+)](c), following either depolarisation or the release of Ca(2+) from the SR (by either InsP(3) or caffeine), were neither voltage nor Na(+) dependent. Thus, no evidence for short term (seconds) control of [Ca(2+)](c) by the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger was found. Together, the results suggest that despite the lack of CICR, the SR removes Ca(2+) from the cytosol after its elevation by depolarisation. This Ca(2+) is then removed from the SR to outside the cell by the Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger. However, the exchanger does not contribute significantly to the decline in bulk average [Ca(2+)](c) following transient elevations in the ion produced either by depolarisation or by release from the store.
Figures



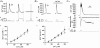
References
-
- Ahn SC, Lee SJ, Goo YS, Sim JH, So I, Kim KW. Protein kinase C suppresses spontaneous, transient, outwards K+ currents through modulation of the Na/Ca exchanger in guinea-pig gastric myocytes. Pflügers Archiv. 2001;441:417–424. - PubMed
-
- Arnon A, Hamlyn JM, Blaustein MP. Ouabain augments Ca2+ transients in arterial smooth muscle without raising cytosolic Na+ American Journal of Physiology. 2000;279:H679–691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

