Whisker maps of neuronal subclasses of the rat ventral posterior medial thalamus, identified by whole-cell voltage recording and morphological reconstruction
- PMID: 11790815
- PMCID: PMC2290066
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.012334
Whisker maps of neuronal subclasses of the rat ventral posterior medial thalamus, identified by whole-cell voltage recording and morphological reconstruction
Abstract
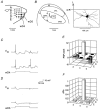
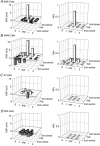
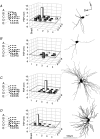
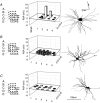
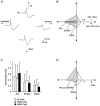
Whole-cell voltage recordings were made in vivo in the ventral posterior medial nucleus (VPM) of the thalamus in urethane-anaesthetised young (postnatal day 16-24) rats. Receptive fields (RFs) on the whisker pad were mapped for 31 neurones, and 10 cells were recovered for morphological reconstruction of their dendritic arbors. Most VPM neurones had antagonistic subthreshold RFs that could be divided into excitatory and inhibitory whiskers. VPM cells comprised different classes, the most frequently occurring being single-whisker excitation (SWE) and multi-whisker excitation (MWE) cells. In SWE cells (36 % of VPM neurones), only principal whisker (PW) deflection evoked an EPSP and was followed by a single action potential (AP) or remained subthreshold. The depolarisation was terminated by a large, delayed IPSP. A stimulus evoked on average 0.74 +/- 0.46 APs (mean +/- S.D.) with short latency (8.1 +/- 1.0 ms) and small temporal scatter (0.31 +/- 0.23 ms dispersion of 50 % of the first APs). In MWE cells (29 % of VPM neurones), deflection of several whiskers evoked EPSPs. PW responses were either subthreshold EPSPs or consisted of an EPSP followed by one or several APs (0.96 +/- 0.99 APs per stimulus). AP responses were often associated with putative low-threshold calcium-dependent regenerative potentials and were followed by a small delayed IPSP. AP responses had a longer latency (12.3 +/- 2.6 ms) and larger temporal scatter (2.5 +/- 1.6 ms) than responses of SWE cells. MWE cells had a lower input resistance than SWE cells. The elongation of dendritic arbors along the representation fields of rows and arcs in VPM barreloids was weakly correlated with the subthreshold RF elongation along whisker rows and arcs, respectively. Evoked EPSP-AP responses exhibited a sharper directional tuning than subthreshold EPSPs, which in turn exhibited a sharper directional tuning than IPSPs. In conclusion, we document two main classes of VPM neurones. SWE cells responded with a precisely timed single AP to the deflection of the PW. In contrast, MWE cell RFs were more broadly tuned and the temporally dispersed multiple AP responses of these cells represented the degree of collective deflection of the PW and several adjacent whiskers.
Figures







References
-
- Armstrong-James M. The nature and plasticity of sensory processing within adult rat barrel cortex. In: Jones EG, Diamond IT, editors. The Barrel Cortex of Rodents. New York: Plenum; 1995. pp. 333–374.
-
- Armstrong M, Callahan C. Thalamocortical mechanisms in the formation of receptive fields of rat barrel cortex neurones. II. Spatiotemporal convergence in the thalamic ventroposterior medial nucleus (VPm) and its relevance to generation of receptive fields of S1 cortical “barrel” neurones. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1991;303:211–224. - PubMed
-
- Arnold PB, Li CX, Waters RS. Thalocortical arbors extend beyond single cortical barrels: an in vivo tracing study in the rat. Experimental Brain Research. 2001;136:152–168. - PubMed
-
- Barbaresi P, Spreafico R, Frassoni C, Rustioni A. GABA-ergic neurons are present in the dorsal column nuclei but not in the ventroposterior complex of rats. Brain Research. 1986;382:305–326. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

