Low levels of asparagine deamidation can have a dramatic effect on aggregation of amyloidogenic peptides: implications for the study of amyloid formation
- PMID: 11790844
- PMCID: PMC2373442
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.48702
Low levels of asparagine deamidation can have a dramatic effect on aggregation of amyloidogenic peptides: implications for the study of amyloid formation
Abstract
The polypeptide hormone amylin forms amyloid deposits in Type 2 diabetes mellitus and a 10-residue fragment of amylin (amylin(20-29)) is commonly used as a model system to study this process. Studies of amylin(20-29) and several variant peptides revealed that low levels of deamidation can have a significant effect on the secondary structure and aggregation behavior of these molecules. Results obtained with a variant of amylin(20-29), which has the primary sequence SNNFPAILSS, are highlighted. This peptide is particularly interesting from a technical standpoint. In the absence of impurities the peptide does not spontaneously aggregate and is not amyloidogenic. This peptide can spontaneously deamidate, and the presence of less than 5% of deamidation impurities leads to the formation of aggregates that have the hallmarks of amyloid. In addition, small amounts of deamidated material can induce amyloid formation by the purified peptide. These results have fundamental implications for the definition of an amyloidogenic sequence and for the standards of purity of peptides and proteins used for studies of amyloid formation.
Figures

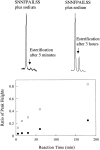

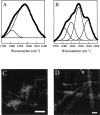

References
-
- Ashburn, T.T. and Lansbury, P.T., Jr. 1993. Interspecies sequence variations affect the kinetics and thermodynamics of amyloid formation: Peptide models of pancreatic amyloid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 11511012–11013.
-
- Ashburn, T.T., Auger, M., 1st., and Lansbury, P.T., Jr. 1992. The structural basis of pancreatic amyloid formation: Isotope-edited spectroscopy in the solid state. J. Am. Chem. Soc. BO114: 790–791.
-
- Aswad, D.W. and Guzetta, A.W. 1995. Methods for analysis of deamidation and isoaspartate formation in peptides and proteins. In Deamidation and isoaspartate formation in peptides and proteins (ed. D.W. Aswad), pp. 8–29. CRC Press, Ann Arbor, MI.
-
- Baumann, M.H., Wisniewski, T., Levy, E., Plant, G.T., and Ghiso, J. 1996. C-terminal fragments of alpha- and beta-tubulin form amyloid fibrils in vitro and associate with amyloid deposits of familial cerebral amyloid angiopathy, British type. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 219238–242. - PubMed
-
- Betsholtz, C., Christmansson, L., Engstrom, U., Rorsman, F., Jordan, K., O'Brien, T.D., Murtaugh, M., Johnson, K.H., and Westermark, P. 1990. Structure of cat islet polypeptide and identification of amino acid residues of potential significance for islet amyloid formation. Diabetes 39 118–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

