Genomewide search for type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility loci in Finnish families: the Botnia study
- PMID: 11791216
- PMCID: PMC384923
- DOI: 10.1086/338629
Genomewide search for type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility loci in Finnish families: the Botnia study
Abstract
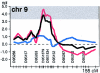
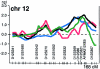
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous inherited disorder characterized by chronic hyperglycemia resulting from pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Although the pathogenic mechanisms are not fully understood, manifestation of the disease most likely requires interaction between both environmental and genetic factors. In the search for such susceptibility genes, we have performed a genomewide scan in 58 multiplex families (comprising 440 individuals, 229 of whom were affected) from the Botnia region in Finland. Initially, linkage between chromosome 12q24 and impaired insulin secretion had been reported, by Mahtani et al., in a subsample of 26 families. In the present study, we extend the initial genomewide scan to include 32 additional families, update the affectation status, and fine map regions of interest, and we try to replicate the initial stratification analysis. In our analysis of all 58 families, we identified suggestive linkage to one region, chromosome 9p13-q21 (nonparametric linkage [NPL] score 3.9; P<.0002). Regions with nominal P values <.05 include chromosomes 2p11 (NPL score 2.0 [P<.03]), 3p24-p22 (NPL score 2.2 [P<.02]), 4q32-q33 (NPL score 2.5 [P<.01]), 12q24 (NPL score 2.1 [P<.03]), 16p12-11 (NPL score 1.7 [P<.05]), and 17p12-p11 (NPL score 1.9 [P<.03]). When chromosome 12q24 was analyzed in only the 32 additional families, a nominal P value <.04 was observed. Together with data from other published genomewide scans, these findings lend support to the hypothesis that regions on chromosome 9p13-q21 and 12q24 may harbor susceptibility genes for type 2 diabetes.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GENEHUNTER software-distribution web site, http://www.genome.wi.mit.edu/ftp/distribution/software/gh2/
-
- Human Genetics Group web site, http://www-genome.wi.mit.edu/humgen/ (for raw data)
-
- International Type 2 Diabetes Linkage Analysis Consortium, http://www.sfbr.org/external/diabetes/ - PMC - PubMed
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for CAPN10 [MIM 605286], NIDDM1 [MIM 601283], and NIDDM2 [MIM 601407], and PPARγ [MIM 601487])
References
-
- Alberti KG, Gries FA (1988) Management of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Europe: a consensus view. Diabet Med 5:275–281 - PubMed
-
- Altshuler D, Hirschhorn JN, Klannemark M, Lindgren CM, Vohl MC, Nemesh J, Lane CR, Schaffner SF, Bolk S, Brewer C, Tuomi T, Gaudet D, Hudson TJ, Daly M, Groop L, ES L (2000) The common PPARgamma Pro12Ala polymorphism is associated with decreased risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 26:76–80 - PubMed
-
- Bektas A, Suprenant ME, Wogan LT, Plengvidhya N, Rich SS, Warram JH, Krolewski AS, Doria A (1999) Evidence of a novel type 2 diabetes locus 50 cM centromeric to NIDDM2 on chromosome 12q. Diabetes 48:2246–2251 - PubMed
-
- Bowden DW, Sale M, Howard TD, Qadri A, Spray BJ, Rothschild CB, Akots G, Rich SS, Freedman BI (1997) Linkage of genetic markers on human chromosomes 20 and 12 to NIDDM in Caucasian sib pairs with a history of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 46:882–886 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

