Efficacy of ceftriaxone and gentamicin given once a day by using human-like pharmacokinetics in treatment of experimental staphylococcal endocarditis
- PMID: 11796345
- PMCID: PMC127055
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.46.2.378-384.2002
Efficacy of ceftriaxone and gentamicin given once a day by using human-like pharmacokinetics in treatment of experimental staphylococcal endocarditis
Abstract
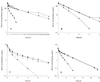
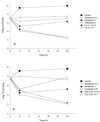
We compared the efficacy of ceftriaxone combined with gentamicin, both given once a day, with that of cloxacillin given every 4 h plus gentamicin given once a day or in three daily doses (t.i.d.) for the treatment of experimental methicillin-susceptible staphylococcal endocarditis. The antibiotics were administered by using human-like (H-L) pharmacokinetics that simulated the profiles of these drugs in human serum. Animals with catheter-induced endocarditis were infected intravenously with 10(5) CFU of Staphylococcus aureus S5 (MICs and minimal bactericidal concentrations of cloxacillin, ceftriaxone, and gentamicin, 0.5 and 2 microg/ml, 4 and 8 microg/ml, and 0.5 and 1 microg/ml, respectively). The animals were then treated for 24 h with cloxacillin at a dose of 2 g that simulated H-L pharmacokinetics (H-L 2 g) every 4 h alone or combined with gentamicin (administered at doses of H-L 1 mg/kg of body weight every 8 h or H-L 4.5 mg/kg every 24 h) or with ceftriaxone at H-L 2 g every 24 h alone or combined with gentamicin (administered at doses of H-L 1 mg/kg every 8 h or H-L 4.5 mg/kg every 24 h). The results of therapy for experimental endocarditis due to the S5 strain showed that (i) cloxacillin alone is more effective than ceftriaxone alone in reducing the bacterial load (P < 0.01), (ii) the combination of cloxacillin or ceftriaxone with gentamicin is more effective than each of these drugs alone (P < 0.01), and (iii) Ceftriaxone H-L plus gentamicin H-L 4.5 mg/kg, both administered every 24 h, showed efficacy similar to that of the "gold standard," cloxacillin H-L plus gentamicin H-L 1 mg/kg t.i.d. (P > 0.05). An increase in the interval of administration of gentamicin to once daily resulted in a reduction in the numbers of bacteria in the vegetations equivalent to that achieved with the recommended regimen of cloxacillin plus gentamicin t.i.d. in the treatment of experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-susceptible S. aureus. Ceftriaxone plus gentamicin, both administered once a day, may be useful for home-based therapy for selected cases of staphylococcal endocarditis.
Figures
References
-
- Bisno, A. L., W. E. Dismukes, D. T. Durack, E. L. Kaplan, A. W. Karchmer, D. Kaye, S. H. Rahimtoola, M. A. Sande, J. P. Sandford, C. Watanakunakorn, and W. R. Wilson. 1989. Antimicrobial treatment of infective endocarditis due to viridans streptococci, enterococci and staphylococci. JAMA 261:1471-1477. - PubMed
-
- Campos, M. E., S. Rabinovich, and I. M. Smith. 1974. Therapy of experimental staphylococcal infection with antibiotic combinations. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 83:241-248. - PubMed
-
- Dhawan, V. K., H. Thadepalli, M. K. Maier, M. Nayyar, M. B. Bansal, and S. K. Chuah. 1984. Newer beta-lactam antibiotics in the treatment of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 14:165-169. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

