Left ventricular long axis function in diastolic heart failure is reduced in both diastole and systole: time for a redefinition?
- PMID: 11796546
- PMCID: PMC1766981
- DOI: 10.1136/heart.87.2.121
Left ventricular long axis function in diastolic heart failure is reduced in both diastole and systole: time for a redefinition?
Abstract
Objective: To test the hypothesis that, when measured in the long axis, left ventricular systolic function is abnormal in patients with diastolic heart failure.
Design: A case-control study.
Setting: University teaching hospital (tertiary referral centre).
Patients: 68 patients with heart failure, 29 with a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of > 0.45 and diastolic dysfunction (diastolic heart failure), 39 with an LVEF of </= 0.45 (systolic heart failure), and 105 normal subjects, including 33 age matched controls.
Methods: LVEF was measured by cross sectional Simpson's method, and mitral annular amplitudes and velocities by M mode and tissue Doppler echocardiography, respectively, along with mitral Doppler inflow velocities. Results were compared between the three groups.
Main outcome measures: Peak systolic mitral annular velocity and amplitude between the different groups.
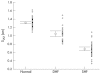
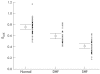
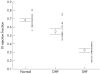
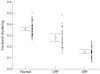
Results: The mitral annular peak mean velocity and amplitude in systole were lower in the patients with diastolic heart failure (mean (SEM), 4.8 (0.2) cm/s) than in the age matched normal controls (6.1 (0.14) cm/s), but higher than those with systolic heart failure (2.8 (0.13) cm/s) (all p < 0.001). Similar changes were seen the mitral annular amplitude during systole. Peak early diastolic velocity and amplitude were also significantly reduced in the group with diastolic heart failure. Left ventricular hypertrophy was evident in over 95% patients in both diastolic and systolic heart failure groups, with a comparable left ventricular mass index.
Conclusions: In patients with diastolic heart failure and evidence of left ventricular hypertrophy, there is systolic left ventricular impairment as measured by myocardial Doppler imaging of the longitudinal axis. Thus subtle abnormalities of systolic function are present in patients with heart failure and a normal left ventricular ejection fraction, and there appears to be a continuum of systolic function between those with truly normal, mildly impaired (labelled diastolic heart failure), and obviously abnormal left ventricular systolic function. Isolated diastolic dysfunction is uncommon.
Figures


References
-
- Yip GWK, Ho PPY, Woo KS, et al. Comparison of frequencies of left ventricular systolic and diastolic heart failure in Chinese living in Hong Kong. Am J Cardiol 1999;84:563–7. - PubMed
-
- Yu CM, Sanderson JE. Right and left ventricular diastolic function in patients with and without heart failure: effect of age, sex, heart rate, and respiration on Doppler-derived measurements. Am Heart J 1997;134:426–34. - PubMed
-
- European Study Group on Diastolic Heart Failure. Working Group Report: How to diagnose diastolic heart failure. Eur Heart J 1998;19:990–1003. - PubMed
-
- Henry WL, De Maria A, Gramiak R, et al. Report of the American Society of Echocardiography Committee on nomenclature and standards in 2-D echocardiography. Circulation 1980;62:212–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
