CD8(+)-T-cell immunity against Toxoplasma gondii can be induced but not maintained in mice lacking conventional CD4(+) T cells
- PMID: 11796568
- PMCID: PMC127655
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.434-443.2002
CD8(+)-T-cell immunity against Toxoplasma gondii can be induced but not maintained in mice lacking conventional CD4(+) T cells
Abstract
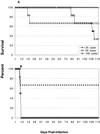
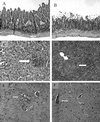
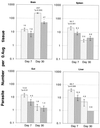
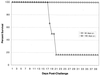
T-cell immunity is critical for survival of hosts infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Among the cells in the T-cell population, CD8(+) T cells are considered the major effector cells against this parasite. It is believed that CD4(+) T cells may be crucial for induction of the CD8(+)-T-cell response against T. gondii. In the present study, CD4(-/-) mice were used to evaluate the role of conventional CD4(+) T cells in the immune response against T. gondii infection. CD4(-/-) mice infected with T. gondii exhibited lower gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) messages in the majority of their tissues. As a result, mortality due to a hyperinflammatory response was prevented in these animals. Interestingly, T. gondii infection induced a normal antigen-specific CD8(+)-T-cell immune response in CD4(-/-) mice. No difference in generation of precursor cytotoxic T lymphocytes (pCTL) or in IFN-gamma production by the CD8(+)-T-cell populations from the knockout and wild-type animals was observed. However, the mutant mice were not able to sustain CD8(+)-T-cell immunity. At 180 days after infection, the CD8(+)-T-cell response in the knockout mice was depressed, as determined by pCTL and IFN-gamma assays. Loss of CD8(+)-T-cell immunity at this time was confirmed by adoptive transfer experiments. Purified CD8(+) T cells from CD4(-/-) donors that had been immunized 180 days earlier failed to protect the recipient mice against a lethal infection. Our study demonstrated that although CD8(+)-T-cell immunity can be induced in the absence of conventional CD4(+) T cells, it cannot be maintained without such cells.
Figures


References
-
- Andersen, H., D. Dempsey, R. Chervenak, and S. R. Jennings. 2000. Expression of intracellular IFN-gamma in HSV-1-specific CD8+ T cells identifies distinct responding subpopulations during the primary response to infection. J. Immunol. 165:2101–2107. - PubMed
-
- Cho, S., V. Mehra, S. Thoma-Uszynski, S. Stenger, N. Serbina, R. J. Mazzaccaro, J. L. Flynn, P. F. Barnes, S. Southwood, E. Celis, B. R. Bloom, R. L. Modlin, and A. Sette. 2000. Antimicrobial activity of MHC class I-restricted CD8+ T cells in human tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:12210–12215. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Denkers, E. Y., T. Scharton-Kersten, S. Barbieri, P. Caspar, and A. Sher. 1996. A role for CD4+ NK1.1+ T lymphocytes as major histocompatibility complex class II independent helper cells in the generation of CD8+ effector function against intracellular infection. J. Exp. Med. 184:131–139. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

