Molecular analysis of group B protective surface protein, a new cell surface protective antigen of group B streptococci
- PMID: 11796614
- PMCID: PMC127721
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.803-811.2002
Molecular analysis of group B protective surface protein, a new cell surface protective antigen of group B streptococci
Abstract
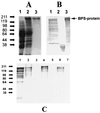
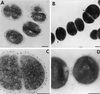
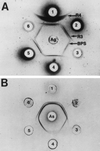
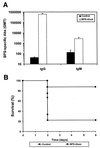
Group B streptococci (GBS) express various surface antigens designated c, R, and X antigens. A new R-like surface protein from Streptococcus agalactiae strain Compton R has been identified by using a polyclonal antiserum raised against the R protein fraction of this strain to screen a lambda Zap library. DNA sequence analysis of positive clones allowed the prediction of the primary structure of a 105-kDa protein designated BPS protein (group B protective surface protein) that exhibited typical features of streptococcal surface proteins such as a signal sequence and a membrane anchor region but did not show significant similarity with other known sequences. Immunogold electron microscopy using a BPS-specific antiserum confirmed the surface location of BPS protein on S. agalactiae strain Compton R. Anti-BPS antibodies did not cross-react with R1 and R4 proteins expressed by two variant type III GBS strains but reacted with the parental streptococcal strain in Western blot and immunoprecipitation analyses. Separate R3 and BPS immunoprecipitation bands were observed when a cell extract of strain Compton R was tested with an antiserum against Compton R previously cross-absorbed to remove R4 antibodies. Immunization of mice with recombinant BPS protein by the subcutaneous route produced an efficient antigen-specific response, and immunized animals survived challenge with a lethal dose of a virulent strain. Therefore, BPS protein represents a new R-like protective antigen of GBS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Putative novel surface-exposed Streptococcus agalactiae protein frequently expressed by the group B streptococcus from Zimbabwe.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009 Sep;16(9):1302-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00133-09. Epub 2009 Jul 8. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19587152 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of repeats in the alpha C protein enhances the pathogenicity of group B streptococci in immune mice.Infect Immun. 1998 Sep;66(9):4347-54. doi: 10.1128/IAI.66.9.4347-4354.1998. Infect Immun. 1998. PMID: 9712787 Free PMC article.
-
Cloned alpha and beta C-protein antigens of group B streptococci elicit protective immunity.Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2023-8. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2023-2028.1991. Infect Immun. 1991. PMID: 1674738 Free PMC article.
-
A protective surface protein from type V group B streptococci shares N-terminal sequence homology with the alpha C protein.Infect Immun. 1996 Oct;64(10):4255-60. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.10.4255-4260.1996. Infect Immun. 1996. PMID: 8926097 Free PMC article.
-
Surface-localized protein antigens of group B streptococci.Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 Suppl 2:S363-6. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s363. Rev Infect Dis. 1988. PMID: 3055205 Review.
Cited by
-
Putative novel surface-exposed Streptococcus agalactiae protein frequently expressed by the group B streptococcus from Zimbabwe.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009 Sep;16(9):1302-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00133-09. Epub 2009 Jul 8. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19587152 Free PMC article.
-
Survey of immunological features of the alpha-like proteins of Streptococcus agalactiae.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Feb;22(2):153-9. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00643-14. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25540270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptococcus agalactiae alpha-like protein 1 possesses both cross-reacting and Alp1-specific epitopes.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011 Aug;18(8):1365-70. doi: 10.1128/CVI.05005-11. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21653744 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological markers of the R4 protein of Streptococcus agalactiae.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2005 Nov;12(11):1305-10. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.12.11.1305-1310.2005. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16275945 Free PMC article.
-
Progress toward a group B streptococcal vaccine.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018;14(11):2669-2681. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1493326. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2018. PMID: 29995578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker, C. J., and M. S. Edwards. 1995. Group B streptococcal infections, p. 980-1054. In J. S. Remington and J. O. Klein (ed.), Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant. W. B. Saunders, Philadelphia, Pa.
-
- Baker, C. J., and D. L. Kasper. 1976. Correlation of maternal antibody deficiency with susceptibility to neonatal group B streptococcal infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 294:753-756. - PubMed
-
- Baker, C. J., M. A. Rench, M. S. Edwards, R. J. Carpenter, B. M. Hays, and D. L. Kasper. 1988. Immunization of pregnant women with a polysaccharide vaccine of group B Streptococcus. N. Engl. J. Med. 319:1180-1185. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, M. M. 1979. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248-254. - PubMed
-
- Burnette, W. N. 1981. “Western blotting”: electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radiolabelled protein A. Anal. Biochem. 112:195-203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

