Adenovirus E3-6.7K maintains calcium homeostasis and prevents apoptosis and arachidonic acid release
- PMID: 11799152
- PMCID: PMC135875
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.4.1578-1587.2002
Adenovirus E3-6.7K maintains calcium homeostasis and prevents apoptosis and arachidonic acid release
Abstract
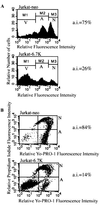
E3-6.7K is a small and hydrophobic membrane glycoprotein encoded by the E3 region of subgroup C adenovirus. Recently, E3-6.7K has been shown to be required for the downregulation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptors by the adenovirus E3/10.4K and E3/14.5K complex of proteins. We demonstrate here that E3-6.7K has additional protective roles, independent of other virus proteins. In transfected Jurkat T-cell lymphoma cells, E3-6.7K was found to maintain endoplasmic reticulum-Ca(2+) homeostasis and inhibit the induction of apoptosis by thapsigargin. The presence of E3-6.7K also lead to a reduction in the TNF-induced release of arachidonic acid from transfected U937 human histiocytic lymphoma cells. In addition, E3-6.7K protected cells against apoptosis induced through Fas, TNF receptor, and TRAIL receptors. Therefore, E3-6.7K confers a wide range of protective effects against both Ca(2+) flux-induced and death receptor-mediated apoptosis.
Figures
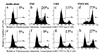




Similar articles
-
The adenovirus E3-14.7K protein and the E3-10.4K/14.5K complex of proteins, which independently inhibit tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced apoptosis, also independently inhibit TNF-induced release of arachidonic acid.J Virol. 1996 Aug;70(8):4904-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.8.4904-4913.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8763993 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel immunosubversion mechanism mediated by a virologue of the B-lymphocyte receptor TACI.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Jul;14(7):907-17. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00058-07. Epub 2007 May 30. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17538121 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus E3-10.4K/14.5K protein complex inhibits tumor necrosis factor-induced translocation of cytosolic phospholipase A2 to membranes.J Virol. 1997 Apr;71(4):2830-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.4.2830-2837.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9060638 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus genes that modulate the sensitivity of virus-infected cells to lysis by TNF.J Cell Biochem. 1993 Dec;53(4):329-35. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240530410. J Cell Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8300750 Review.
-
Functions and mechanisms of action of the adenovirus E3 proteins.Int Rev Immunol. 2004 Jan-Apr;23(1-2):75-111. doi: 10.1080/08830180490265556. Int Rev Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14690856 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct domains in the adenovirus E3 RIDalpha protein are required for degradation of Fas and the epidermal growth factor receptor.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(21):11685-96. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.21.11685-11696.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14557654 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus RIDbeta subunit contains a tyrosine residue that is critical for RID-mediated receptor internalization and inhibition of Fas- and TRAIL-induced apoptosis.J Virol. 2002 Nov;76(22):11329-42. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.22.11329-11342.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12388693 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of apoptosis in Cryptosporidium parvum-infected intestinal epithelial cells is dependent on survivin.Infect Immun. 2008 Aug;76(8):3784-92. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00308-08. Epub 2008 Jun 2. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18519556 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y2 purinergic receptor modulates virus yield, calcium homeostasis, and cell motility in human cytomegalovirus-infected cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Sep 17;116(38):18971-18982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1907562116. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31481624 Free PMC article.
-
A Renaissance for Oncolytic Adenoviruses?Viruses. 2023 Jan 26;15(2):358. doi: 10.3390/v15020358. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andiman, W. A., R. I. Jacobson, and G. Tucker. 1977. Leukocyte-associated viremia with adenovirus type 2 in an infant with lower-respiratory-tract disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 297:100-101. - PubMed
-
- Andiman, W. A., and G. Miller. 1982. Persistent infection with adenovirus types 5 and 6 in lymphoid cells from humans and woolly monkeys. J. Infect. Dis. 145:83-88. - PubMed
-
- Barry, M., S. Hnatiuk, K. Mossman, S. F. Lee, L. Boshkov, and G. McFadden. 1997. The myxoma virus M-T4 gene encodes a novel RDEL-containing protein that is retained within the endoplasmic reticulum and is important for the productive infection of lymphocytes. Virology 239:360-377. - PubMed
-
- Benedict, C. A., K. D. Butrovich, N. S. Lurain, J. Corbeil, I. Rooney, P. Schneider, J. Tschopp, and C. F. Ware. 1999. Cutting edge: a novel viral TNF receptor superfamily member in virulent strains of human cytomegalovirus. J. Immunol. 162:6967-6970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

