Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded G protein-coupled receptor ORF74 constitutively activates p44/p42 MAPK and Akt via G(i) and phospholipase C-dependent signaling pathways
- PMID: 11799169
- PMCID: PMC135879
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.76.4.1744-1752.2002
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded G protein-coupled receptor ORF74 constitutively activates p44/p42 MAPK and Akt via G(i) and phospholipase C-dependent signaling pathways
Abstract
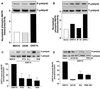
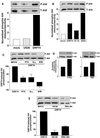
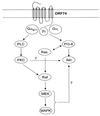
The G protein-coupled receptor encoded by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, also referred to as ORF74, has been shown to stimulate oncogenic and angiogenic signaling pathways in a constitutively active manner. The biochemical routes linking ORF74 to these signaling pathways are poorly defined. In this study, we show that ORF74 constitutively activates p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and Akt via G(i)- and phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated signaling pathways. Activation of Akt by ORF74 appears to be phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K) dependent but, interestingly, is also mediated by activation of protein kinase C (PKC) and p44/p42 MAPK. ORF74 may signal to Akt via p44/p42 MAPK, which can be activated by G(i), through activation of PI3-K or through PKC via the PLC pathway. Signaling of ORF74 to these proliferative and antiapoptotic signaling pathways can be further modulated positively by growth-related oncogene (GROalpha/CXCL1) and negatively by human gamma interferon-inducible protein 10 (IP-10/CXCL10), thus acting as an agonist and an inverse agonist, respectively. Despite the ability of the cytomegalovirus-encoded chemokine receptor US28 to constitutively activate PLC, this receptor does not increase phosphorylation of p44/p42 MAPK or Akt in COS-7 cells. Hence, ORF74 appears to signal through a larger diversity of G proteins than US28, allowing it to couple to proliferative and antiapoptotic signaling pathways. ORF74 can therefore be envisioned as an attractive target for novel treatment of Kaposi's sarcoma.
Figures
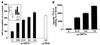
Similar articles
-
Differential activation of murine herpesvirus 68- and Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded ORF74 G protein-coupled receptors by human and murine chemokines.J Virol. 2004 Apr;78(7):3343-51. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.7.3343-3351.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15016856 Free PMC article.
-
The viral G protein-coupled receptor ORF74 unmasks phospholipase C signaling of the receptor tyrosine kinase IGF-1R.Cell Signal. 2016 Jun;28(6):595-605. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.02.017. Epub 2016 Feb 27. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 26931381
-
Activation of NF-kappaB by the human herpesvirus 8 chemokine receptor ORF74: evidence for a paracrine model of Kaposi's sarcoma pathogenesis.J Virol. 2001 Sep;75(18):8660-73. doi: 10.1128/jvi.75.18.8660-8673.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11507211 Free PMC article.
-
Akt/TSC/mTOR activation by the KSHV G protein-coupled receptor: emerging insights into the molecular oncogenesis and treatment of Kaposi's sarcoma.Cell Cycle. 2007 Feb 15;6(4):438-43. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.4.3843. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17329974 Review.
-
Multiple pathways of ERK activation by G protein-coupled receptors.Novartis Found Symp. 2001;239:68-79; discussion 80-4, 150-9. doi: 10.1002/0470846674.ch7. Novartis Found Symp. 2001. PMID: 11529317 Review.
Cited by
-
Manipulation of the host cell membrane by human γ-herpesviruses EBV and KSHV for pathogenesis.Virol Sin. 2016 Oct;31(5):395-405. doi: 10.1007/s12250-016-3817-2. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Virol Sin. 2016. PMID: 27624182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfotyrosines of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus G protein-coupled receptor promote tumorigenesis through autocrine activation.J Virol. 2010 Apr;84(7):3351-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01939-09. Epub 2010 Jan 27. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20106924 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-like tumors in a human herpesvirus 8 ORF74 transgenic mouse.J Virol. 2003 Feb;77(4):2631-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2631-2639.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12552002 Free PMC article.
-
Cancers associated with human gammaherpesviruses.FEBS J. 2022 Dec;289(24):7631-7669. doi: 10.1111/febs.16206. Epub 2021 Oct 2. FEBS J. 2022. PMID: 34536980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular genetics of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus-8) epidemiology and pathogenesis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003 Jun;67(2):175-212, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.2.175-212.2003. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12794189 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adomeit, A., A. Graness, S. Gross, K. Seedorf, R. Wetzker, and C. Liebmann. 1999. Bradykinin B2 receptor-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in COS-7 cells requires dual signaling via both protein kinase C pathway and epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19:5289-5297. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andjelkovic, M., D. R. Alessi, R. Meier, A. Fernandez, N. J. Lamb, M. Frech, P. Cron, P. Cohen, J. M. Lucocq, and B. A. Hemmings. 1997. Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. J. Biol. Chem. 272:31515-31524. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitakis, L., E. Geras-Raaka, A. Varma, M. C. Gershengorn, and E. Cesarman. 1997. Human herpesvirus KSHV encodes a constitutively active G-protein-coupled receptor linked to cell proliferation. Nature 385:347-350. - PubMed
-
- Bais, C., B. Santomasso, O. Coso, L. Aranitakis, E. Geras-Raaka, J. S. Gutkind, A. S. Asch, E. Cesarman, M. C. Gerhengorn, and E. A. Mesri. 1998. G-protein-coupled receptor of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is a viral oncogene and angiogenesis activator. Nature 391:86-89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

