Homozygous defects in LMNA, encoding lamin A/C nuclear-envelope proteins, cause autosomal recessive axonal neuropathy in human (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disorder type 2) and mouse
- PMID: 11799477
- PMCID: PMC384949
- DOI: 10.1086/339274
Homozygous defects in LMNA, encoding lamin A/C nuclear-envelope proteins, cause autosomal recessive axonal neuropathy in human (Charcot-Marie-Tooth disorder type 2) and mouse
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet 2002 Apr;70(4):1075
Abstract
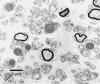
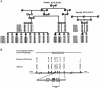
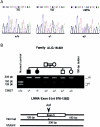
The Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disorders comprise a group of clinically and genetically heterogeneous hereditary motor and sensory neuropathies, which are mainly characterized by muscle weakness and wasting, foot deformities, and electrophysiological, as well as histological, changes. A subtype, CMT2, is defined by a slight or absent reduction of nerve-conduction velocities together with the loss of large myelinated fibers and axonal degeneration. CMT2 phenotypes are also characterized by a large genetic heterogeneity, although only two genes---NF-L and KIF1Bbeta---have been identified to date. Homozygosity mapping in inbred Algerian families with autosomal recessive CMT2 (AR-CMT2) provided evidence of linkage to chromosome 1q21.2-q21.3 in two families (Zmax=4.14). All patients shared a common homozygous ancestral haplotype that was suggestive of a founder mutation as the cause of the phenotype. A unique homozygous mutation in LMNA (which encodes lamin A/C, a component of the nuclear envelope) was identified in all affected members and in additional patients with CMT2 from a third, unrelated family. Ultrastructural exploration of sciatic nerves of LMNA null (i.e., -/-) mice was performed and revealed a strong reduction of axon density, axonal enlargement, and the presence of nonmyelinated axons, all of which were highly similar to the phenotypes of human peripheral axonopathies. The finding of site-specific amino acid substitutions in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 1B, autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, dilated cardiomyopathy type 1A, autosomal dominant partial lipodystrophy, and, now, AR-CMT2 suggests the existence of distinct functional domains in lamin A/C that are essential for the maintenance and integrity of different cell lineages. To our knowledge, this report constitutes the first evidence of the recessive inheritance of a mutation that causes CMT2; additionally, we suggest that mutations in LMNA may also be the cause of the genetically overlapping disorder CMT2B1.
Figures
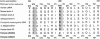

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- BLAST, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/ (for BLASTP)
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for A1U [accession number AF188240], FLJ12287 [accession number AK022349], LMNA [accession number XM_044163], mouse SemB [accession number X85991], lamin A/C mRNA [accession number XM_044163], lamin B1 mRNA [accession number AAC37575], mouse lamin A [accession number P48678], chicken lamin A [accession number P13648], X. laevis lamin A [accession number P11048], D. melanogaster DMO [accession number P08928], C. elegans lamin [accession number S42257], and genomic LMNA sequence contained in a BAC contig [accession number NT004858])
-
- Généthon, ftp://ftp.genethon.fr/pub/Gmap/Nature-1995/ (for genetic map)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for CMT2E [MIM 162280], CMT2A [MIM 118210], CMT1B [MIM 118200], Dejerine-Sottas disease [MIM 145900], congenital hypomyelination [MIM 605253], CMT2B1 [MIM 605588], CMT2B2 [MIM 605589], LGMD1B [MIM 159001], AD-EDMD [MIM 181350], CMD1A [MIM 115200], and PLD [MIM 151660])
-
- PROSITE: Database of Protein Families and Domains, http://www.expasy.ch/prosite/
References
-
- Barhoumi C, Amouri R, Ben Hamida C, Ben Hamida M, Machghoul S, Gueddiche M, Hentati F (2001) Linkage of a new locus for autosomal recessive axonal form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease to chromosome 8q21.3. Neuromuscul Disord 11:27–34 - PubMed
-
- Bolino A, Muglia M, Conforti FL, LeGuern E, Salih MA, Georgiou DM, Christodoulou K, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I, Mandich P, Schenone A, Gambardella A, Bono F, Quattrone A, Devoto M, Monaco AP (2000) Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4B is caused by mutations in the gene encoding myotubularin-related protein-2. Nat Genet 25:17–19 - PubMed
-
- Bonne G, Raffaele di Barletta M, Varnous S, Bécane HM, Hammouda EH, Merlini L, Muntoni F, Greenberg CR, Gary F, Urtizberea JA, Duboc D, Fardeau M, Toniolo D, Schwartz K (1999) Mutations in the gene encoding lamin A/C cause autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet 21:285–288 - PubMed
-
- Brown CA, Lanning RW, McKinney KQ, Salvino AR, Cherniske E, Crowe CA, Darras BT, Gominak S, Greenberg CR, Grosmann C, Heydemann P, Mendell JR, Pober BR, Sasaki T, Shapiro F, Simpson DA, Suchowersky O, Spence JE (2001) Novel and recurrent mutations in lamin A/C in patients with Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Am J Med Genet 102:359–367 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

