Optimization-based models of muscle coordination
- PMID: 11800497
- PMCID: PMC2821033
- DOI: 10.1097/00003677-200201000-00007
Optimization-based models of muscle coordination
Abstract
Optimization-based models may provide reasonably accurate estimates of activation and force patterns of individual muscles in selected well-learned tasks with submaximal efforts. Such optimization criteria as minimum energy expenditure, minimum muscle fatigue, and minimum sense of effort seem most promising.
Figures
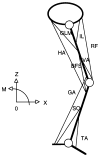
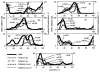
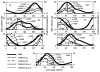
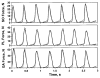
References
-
- Alexander RM. Energy-minimizing choices of muscles and patterns of movement. Motor Control. 2000;4:45–47. - PubMed
-
- An KN, Kwak BM, Chao EY, Morrey BF. Determination of muscle and joint forces: a new technique to solve the indeterminate problem. Trans ASME. 1984;106:364–367. - PubMed
-
- Anderson FC, Pandy MG. Static and dynamic optimization solutions for gait are practically equivalent. J Biomech. 2001;34:153–161. - PubMed
-
- Crowninshield RD, Brand RA. A physiologically based criterion of muscle force prediction in locomotion. J Biomech. 1981;14:793–801. - PubMed
-
- Dul J, Johnson GE, Shiavi R, Townsend MA. Muscular synergism. II. A minimum-fatigue criterion for load sharing between synergistic muscles. J Biomech. 1984;17:675–684. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

