Receptor protein tyrosine kinase EphB4 is up-regulated in colon cancer
- PMID: 11801186
- PMCID: PMC64642
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-2-15
Receptor protein tyrosine kinase EphB4 is up-regulated in colon cancer
Abstract
Background: We have used commercially available cDNA arrays to identify EphB4 as a gene that is up-regulated in colon cancer tissue when compared with matched normal tissue from the same patient.
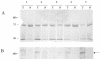
Results: Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the expression of the EphB4 gene has shown that its expression is increased in 82% of tumour samples when compared with the matched normal tissue from the same patient. Using immunohistochemistry and Western analysis techniques with an EphB4-specific antibody, we also show that this receptor is expressed in the epithelial cells of the tumour tissue and either not at all, or in only low levels, in the normal tissue.
Conclusion: The results presented here supports the emerging idea that Eph receptors play a role in tumour formation and suggests that further elucidation of this signalling pathway may identify useful targets for cancer treatment therapies.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Investigation of the expression of the EphB4 receptor tyrosine kinase in prostate carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2005 Sep 20;5:119. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-5-119. BMC Cancer. 2005. PMID: 16171530 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-tumour effects of antibodies targeting the extracellular cysteine-rich region of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphB4.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 10;6(10):7554-69. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3199. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25831049 Free PMC article.
-
Eph receptor B4 is a regulator of estrogen receptor alpha in breast cancer cells.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2013 Aug;33(4):244-8. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2013.795971. Epub 2013 May 31. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2013. PMID: 23725356
-
The EphB4 receptor suppresses breast cancer cell tumorigenicity through an Abl-Crk pathway.Nat Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;8(8):815-25. doi: 10.1038/ncb1438. Epub 2006 Jul 23. Nat Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16862147
-
Paradoxes of the EphB4 receptor in cancer.Cancer Res. 2007 May 1;67(9):3994-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0525. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17483308 Review.
Cited by
-
The tumour-promoting receptor tyrosine kinase, EphB4, regulates expression of integrin-β8 in prostate cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2015 Mar 22;15:164. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1164-6. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25886373 Free PMC article.
-
Competition amongst Eph receptors regulates contact inhibition of locomotion and invasiveness in prostate cancer cells.Nat Cell Biol. 2010 Dec;12(12):1194-204. doi: 10.1038/ncb2122. Epub 2010 Nov 14. Nat Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 21076414
-
Prognostic Value of ACVRL1 Expression in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients Receiving First-line Chemotherapy With Bevacizumab: Results From the Triplet Plus Bevacizumab (TRIBE) Study.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018 Sep;17(3):e471-e488. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2018.03.006. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29636300 Free PMC article.
-
Potential role of the Eph/ephrin system in colorectal cancer: emerging druggable molecular targets.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 2;14:1275330. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1275330. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38651144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The EphB4 receptor tyrosine kinase promotes lung cancer growth: a potential novel therapeutic target.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 2;8(7):e67668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067668. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23844053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maurer CA, Friess H, Kretschmann B, Zimmermann A, Stauffer A, Baer HU, Korc M, Buchler MW. Increased expression of erbB3 in colorectal cancer is associated with concomitant increase in the level of erbB2. Hum Pathol. 1998;29:771–777. - PubMed
-
- Giatromanolaki A, Stathopoulos GP, Tsiobanou E, Papadimitriou C, Georgoulias V, Gatter KC, Harris AL, And Koukourakis MI. Combined role of tumor angiogenesis, bcl-2, and p53 expression in the prognosis of patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 1999;86:1421–1430. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19991015)86:8<1421::AID-CNCR6>3.0.CO;2-X. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

