Heteromultimeric P2X(1/2) receptors show a novel sensitivity to extracellular pH
- PMID: 11805232
- PMCID: PMC5577565
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.300.2.673
Heteromultimeric P2X(1/2) receptors show a novel sensitivity to extracellular pH
Abstract
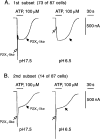
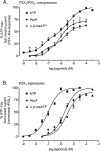
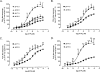
Rat P2X(1) and P2X(2) subunits were coexpressed in defolliculated Xenopus oocytes and the resultant P2X receptors studied under voltage-clamp conditions. Extracellular ATP elicited biphasic inward currents, involving an initial rapidly inactivating (P2X(1)-like) component and a later slowly inactivating (P2X(2)-like) component. The maximum amplitude of P2X(1)-like ATP responses was increased in some cells by lowering extracellular pH (from 7.5 to 6.5), whereas P2X(2)-like responses and those of homomeric rP2X(1) and rP2X(2) receptors were not changed by this treatment. Concentration-response (C/R) curves for ATP for pH-enhanced P2X(1)-like responses were biphasic, and clearly distinct from monophasic ATP C/R curves for homomeric rP2X(1) and rP2X(2) receptors. Under acidic (pH 5.5 and 6.5) and alkaline (pH 8.5) conditions, ATP C/R curves for P2X(1)-like responses showed increases in agonist potency and efficacy, compared with data at pH 7.5, but the same was not true of homomeric rP2X(1) and rP2X(2) receptors. ATP C/R curves for P2X(2)-like responses overlay C/R curves for homomeric rP2X(2) receptors, and determinations of agonist potency and efficacy were identical for P2X(2)-like and P2X(2) responses at all pH levels tested. Our results show that P2X(1)-like responses possessed the kinetics of homomeric P2X(1) receptors but an acid sensitivity different from homomeric P2X(1) and P2X(2) receptors. In contrast, the P2X(2)-like responses exactly matched the profile expected of homomeric P2X(2) receptors. Thus, coexpression of P2X(1) and P2X(2) subunits yielded a mixed population of homomeric and heteromeric P2X receptors, with a subpopulation of novel pH-sensitive P2X receptors showing identifiably unique properties that indicated the formation of heteromeric P2X(1/2) ion channels.
Figures


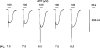
References
-
- Bianchi BR, Lynch KJ, Touma E, Niforatos W, Burgard EC, Alexander KM, Park HS, Yu H, Metzger R, Kowaluk E, et al. Pharmacological characterization of recombinant human and rat P2X receptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;376:127–138. - PubMed
-
- Brake AJ, Wagenbach MJ, Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature (Lond) 1994;371:519–523. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G, King BF. The numbering of cloned P2 purinoceptors. Drug Dev Res. 1996;38:67–71.
-
- Bo X, Zhang Y, Nassar M, Burnstock G, Schoepfer R. A P2X purinoceptor cDNA conferring a novel pharmacological profile. FEBS Lett. 1995;375:129–133. - PubMed
-
- Chen CC, Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Colquhoun D, Burnstock G, Wood JN. A P2X purinoceptor expressed by a subset of sensory neurons. Nature (Lond) 1995;377:428–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

