A quantitative-trait locus in the human factor XII gene influences both plasma factor XII levels and susceptibility to thrombotic disease
- PMID: 11805911
- PMCID: PMC384936
- DOI: 10.1086/339259
A quantitative-trait locus in the human factor XII gene influences both plasma factor XII levels and susceptibility to thrombotic disease
Abstract
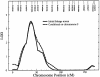
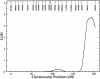
One approach to the identification of genetic loci that influence complex diseases is through the study of quantitative risk factors correlated with disease susceptibility. Factor XII (FXII) plasma levels, a related phenotype correlated with thrombosis, is such a risk factor. We conducted the first genomewide linkage screen to localize genes that influence variation in FXII levels. Two loci were detected: one on chromosome 5 and another on chromosome 10 (LOD scores 4.73 and 3.53, respectively). On chromosome 5, the peak LOD score occurred in the 5q33-5ter region, near the FXII gene. Addition of a 46C/T mutation in the FXII gene increased the multipoint LOD score to 10.21 (P=3.6 x 10(-12)). A bivariate linkage analysis of FXII activity and thrombosis further improved the linkage signal (LOD = 11.73) and provided strong evidence that this quantitative-trait locus (QTL) has a pleiotropic effect on the risk of thrombosis (P=.004). Linkage analysis conditional on 46C/T indicated that this mutation alone cannot explain the chromosome 5 signal, implying that other functional sites must exist. These results represent the first direct genetic evidence that a QTL in or near the FXII gene influences both FXII activity and susceptibility to thrombosis and suggest the presence of one or more still unknown functional variants in FXII.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- ABI-Prism, http://www.appliedbiosystems.com/ (for genetic markers)
-
- Centre National de Genotypage, http://www.cng.fr/ (for genetic markers)
-
- Genome Database, http://www.gdb.org (for genetic markers)
-
- Center for Medical Genetics, Marshfield Medical Research Foundation http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for genetic markers)
-
- Southwest Foundation for Biomedical Research, http://www.sfbr.org/ (for SOLAR program package)
References
-
- Anderson FA, Wheeler HB, Goldberg RJ, Hosmer DW, Forcier A, Patwardhan NA (1991) A population-based perspective of the hospital incidence and case-fatality rates of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: the Worcester DVT Study. Arch Intern Med 151:933–938 - PubMed
-
- Blangero J, Williams JT, Almasy L (2000) Robust LOD scores for variance component-based linkage analysis. Genet Epidemiol Suppl 19:S8–S14 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases