The synucleins
- PMID: 11806835
- PMCID: PMC150459
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2001-3-1-reviews3002
The synucleins
Abstract
Synucleins are small, soluble proteins expressed primarily in neural tissue and in certain tumors. The family includes three known proteins: alpha-synuclein, beta-synuclein, and gamma-synuclein. All synucleins have in common a highly conserved alpha-helical lipid-binding motif with similarity to the class-A2 lipid-binding domains of the exchangeable apolipoproteins. Synuclein family members are not found outside vertebrates, although they have some conserved structural similarity with plant 'late-embryo-abundant' proteins. The alpha- and beta-synuclein proteins are found primarily in brain tissue, where they are seen mainly in presynaptic terminals. The gamma-synuclein protein is found primarily in the peripheral nervous system and retina, but its expression in breast tumors is a marker for tumor progression. Normal cellular functions have not been determined for any of the synuclein proteins, although some data suggest a role in the regulation of membrane stability and/or turnover. Mutations in alpha-synuclein are associated with rare familial cases of early-onset Parkinson's disease, and the protein accumulates abnormally in Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and several other neurodegenerative illnesses. The current challenge is to understand the normal cellular function of these proteins and how they might contribute to the development of human disease.
Figures
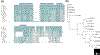

References
-
- Searching GenBank http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/GenbankSearch.html An annotated sequence database maintained by the National Institutes of Health.
-
- Chen X, de Silva HA, Pettenati MJ, Rao PN, St George-Hyslop P, Roses AD, Xia Y, Horsburgh K, Ueda K, Saitoh T. The human NACP/alpha-synuclein gene: chromosome assignment to 4q21.3-q22 and TaqI RFLP analysis. Genomics. 1995;26:425–427. Chromosomal mapping of the α-synuclein gene. - PubMed
-
- Lavedan C. The synuclein family. Genome Res. 1998;8:871–880. A review of the common properties of the synuclein protein family, including gene organization, tissue distribution, and the relationship of protein family members to human disease. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

