Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an epithelial/fibroblastic cross-talk disorder
- PMID: 11806838
- PMCID: PMC64814
- DOI: 10.1186/rr175
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: an epithelial/fibroblastic cross-talk disorder
Abstract
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is a chronic and usually progressive lung disorder of unknown etiology. A growing body of evidence suggests that, in contrast to other interstitial lung diseases, IPF is a distinct entity in which inflammation is a secondary and non-relevant pathogenic partner. Evidence includes the presence of similar mild/moderate inflammation either in early or late disease, and the lack of response to potent anti-inflammatory therapy. Additionally, it is clear from experimental models and some human diseases that it is possible to have fibrosis without inflammation. An evolving hypothesis proposes that IPF may result from epithelial micro-injuries and abnormal wound healing.
Figures
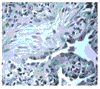
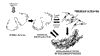
Similar articles
-
Role of epithelial cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: from innocent targets to serial killers.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006 Jun;3(4):364-72. doi: 10.1513/pats.200601-003TK. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006. PMID: 16738202 Review.
-
Evolving concepts of apoptosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006 Jun;3(4):350-6. doi: 10.1513/pats.200601-001TK. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006. PMID: 16738200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The epithelial/fibroblastic pathway in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003 Sep;29(3 Suppl):S93-7. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14503564 Review. No abstract available.
-
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: Primum movens: epithelial, endothelial or whatever.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2005 Dec;22 Suppl 1:S15-23. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2005. PMID: 16457013 Review.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in pulmonary fibrosis.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006 Dec;27(6):600-12. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-957332. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006. PMID: 17195137 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alveolar epithelial cells and microenvironmental stiffness synergistically drive fibroblast activation in three-dimensional hydrogel lung models.Biomater Sci. 2022 Dec 6;10(24):7133-7148. doi: 10.1039/d2bm00827k. Biomater Sci. 2022. PMID: 36366982 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide mediates bleomycin-induced angiogenesis and pulmonary fibrosis via regulation of VEGF.J Cell Biochem. 2015 Nov;116(11):2484-93. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25192. J Cell Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25919965 Free PMC article.
-
Regional differences in susceptibiity of bronchial epithelium to mesenchymal transition and inhibition by the macrolide antibiotic azithromycin.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052309. Epub 2012 Dec 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23284981 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin/CREB binding protein (CBP) signaling reverses pulmonary fibrosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 10;107(32):14309-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001520107. Epub 2010 Jul 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20660310 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of IL-4- and IL-13-responsive cells in pulmonary fibrosis.Immunol Res. 2004;30(3):339-49. doi: 10.1385/IR:30:3:339. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15531774 Review.
References
-
- International consensus statement Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:646–664. - PubMed
-
- Perez-Padilla R, Salas J, Chapela R, Sanchez M, Carrillo G, Perez R, Gaxiola M, Selman M. Mortality in Mexican patients with chronic pigeon breeder's lung compared with those with usual interstitial pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;148:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Bjoraker JA, Ryu JH, Edwin MK, Myers JL, Tazelaar HD, Schroeder DR, Offord KP. Prognostic significance of histopathologic subsets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:199–203. - PubMed
-
- Douglas WW, Ryu JH, Schroeder DR. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Impact of oxygen and colchicine, prednisone, or no therapy on survival. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;161:1172–1178. - PubMed
-
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevaling and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134:136–151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

