Efficacy of school urinary screening for membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type 1
- PMID: 11806875
- PMCID: PMC1719067
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.86.1.21
Efficacy of school urinary screening for membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis type 1
Abstract
Aims: In order to evaluate the efficacy of a school urinary screening programme, children with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) type 1 were studied.
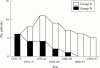
Methods: A total of 52 patients who had been diagnosed with MPGN type 1 from 1970 to 1997 were studied; 35 were identified after 1974 on screening (group S), and 17 were identified by presenting symptoms (group N), mostly before 1989.
Results: Mean blood pressure was 89 mm Hg in group S and 104 mm Hg in group N; urinary protein excretion was 0.9 g/day in group S and 3.0 g/day in group N. Histopathological evidence of chronic changes was found in six group S and 15 group N patients. No patients in group S had renal insufficiency, but five patients in group N required regular haemodialysis.
Conclusions: Results suggest that early identification by school urinary screening may enable early management and so improve prognosis of MPGN.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources