Role for the adaptor protein Grb10 in the activation of Akt
- PMID: 11809791
- PMCID: PMC134632
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.4.979-991.2002
Role for the adaptor protein Grb10 in the activation of Akt
Abstract
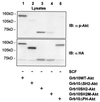
Grb10 is a member of the Grb7 family of adapter proteins lacking intrinsic enzymatic function and encodes functional domains including a pleckstrin homology (PH) domain and an SH2 domain. The role of different Grb10 splice variants in signal transduction of growth factors like insulin or insulin-like growth factor has been described as inhibitory or stimulatory depending on the presence of a functional PH and/or SH2 domain. Performing a yeast two-hybrid screen with the c-kit cytoplasmic tail fused to LexA as a bait and a mouse embryo cDNA library as prey, we found that the Grb10 SH2 domain interacted with the c-kit receptor tyrosine kinase. In the course of SCF-mediated activation of c-kit, Grb10 is recruited to the c-kit receptor in an SH2 domain- and phosphotyrosine-dependent but PH domain-independent manner. We found that Akt and Grb10 form a constitutive complex, suggesting a role for Grb10 in the translocation of Akt to the cell membrane. Indeed, coexpression studies revealed that Grb10 and c-kit activate Akt in a synergistic manner. This dose-dependent effect of Grb10 is wortmannin sensitive and was also seen at a lower level in cells in which c-kit was not expressed. Expression of a Grb10 mutant lacking the SH2 domain as well as a mutant lacking the PH domain did not influence Akt activity. Grb10-induced Akt activation was observed without increased phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) activity, suggesting that Grb10 is a positive regulator of Akt downstream of PI3-kinase. Significantly, deficient activation of Akt by a constitutively activated c-kit mutant lacking the binding site for PI3-kinase (c-kitD814V/Y719F) could be fully compensated by overexpression of Grb10. In Ba/F3 cells, the incapacity of c-kitD814V/Y719F to induce interleukin-3 (IL-3)-independent growth could be rescued by overexpression of Grb10. In contrast, expression of the SH2 deletion mutant of Grb10 together with c-kitD814V/Y719F did not render Ba/F3 cells independent of IL-3. In summary, we provide evidence that Grb10 is part of the c-kit signaling pathway and that the expression level of Grb10 critically influences Akt activity. We propose a model in which Grb10 acts as a coactivator for Akt by virtue of its ability to form a complex with Akt and its SH2 domain-dependent translocation to the cell membrane.
Figures


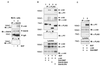







Similar articles
-
Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma activates the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt antiapoptotic signaling pathway.Blood. 2000 Dec 15;96(13):4319-27. Blood. 2000. PMID: 11110708
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase contributes to the transformation of hematopoietic cells by the D816V c-Kit mutant.Blood. 2001 Sep 1;98(5):1365-73. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.5.1365. Blood. 2001. PMID: 11520784
-
Grb10, a positive, stimulatory signaling adapter in platelet-derived growth factor BB-, insulin-like growth factor I-, and insulin-mediated mitogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Sep;19(9):6217-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.9.6217. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10454568 Free PMC article.
-
Grb10 exceeding the boundaries of a common signaling adapter.Front Biosci. 2004 Jan 1;9:603-18. doi: 10.2741/1227. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14766395 Review.
-
Grb10: more than a simple adaptor protein.Front Biosci. 2004 Jan 1;9:387-403. doi: 10.2741/1226. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14766376 Review.
Cited by
-
Crosstalk between PTEN/Akt2 and TGFbeta signaling involving EGF receptor down-regulation during the tumor promotion process from the early stage in a rat two-stage hepatocarcinogenesis model.Cancer Sci. 2009 May;100(5):813-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01120.x. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19309364 Free PMC article.
-
c-Kit-mediated overlapping and unique functional and biochemical outcomes via diverse signaling pathways.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;24(3):1401-10. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.3.1401-1410.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14729982 Free PMC article.
-
Allelic Switching of DLX5, GRB10, and SVOPL during Colorectal Cancer Tumorigenesis.Int J Genomics. 2019 Apr 10;2019:1287671. doi: 10.1155/2019/1287671. eCollection 2019. Int J Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31093489 Free PMC article.
-
The role of small adaptor proteins in the control of oncogenic signalingr driven by tyrosine kinases in human cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 8;7(10):11033-55. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6929. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26788993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akt/PKB interacts with the histone H3 methyltransferase SETDB1 and coordinates to silence gene expression.Mol Cell Biochem. 2007 Nov;305(1-2):35-44. doi: 10.1007/s11010-007-9525-3. Epub 2007 Jun 19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17577629
References
-
- Ahmed, N. N., T. F. Franke, A. Bellacosa, K. Datta, M. E. Gonzalez-Portal, T. Taguchi, J. R. Testa, and P. N. Tsichlis. 1993. The proteins encoded by c-akt and v-akt differ in post-translational modification, subcellular localization and oncogenic potential. Oncogene 8:1957-1963. - PubMed
-
- Altomare, D. A., K. Guo, J. Q. Cheng, G. Sonoda, K. Walsh, and J. R. Testa. 1995. Cloning, chromosomal localization and expression analysis of the mouse Akt2 oncogene. Oncogene 11:1055-1060. - PubMed
-
- Altomare, D. A., G. E. Lyons, Y. Mitsuuchi, J. Q. Cheng, and J. R. Testa. 1998. Akt2 mRNA is highly expressed in embryonic brown fat and the AKT2 kinase is activated by insulin. Oncogene 16:2407-2411. - PubMed
-
- Andjelkovic, M., D. R. Alessi, R. Meier, A. Fernandez, N. J. Lamb, M. Frech, P. Cron, P. Cohen, J. M. Lucocq, and B. A. Hemmings. 1997. Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. J. Biol. Chem. 272:31515-31524. - PubMed
-
- Bai, R. Y., T. Jahn, S. Schrem, G. Munzert, K. M. Weidner, J. Y. Wang, and J. Duyster. 1998. The SH2-containing adapter protein GRB10 interacts with BCR-ABL. Oncogene 17:941-948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
