The hematopoiesis-specific GTP-binding protein RhoH is GTPase deficient and modulates activities of other Rho GTPases by an inhibitory function
- PMID: 11809807
- PMCID: PMC134637
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.4.1158-1171.2002
The hematopoiesis-specific GTP-binding protein RhoH is GTPase deficient and modulates activities of other Rho GTPases by an inhibitory function
Abstract
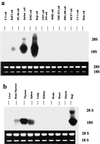
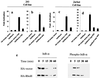
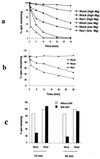
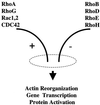
The Rho subfamily of small GTP-binding proteins mediates many fundamental cellular functions. The commonly studied members (Rho, Rac, and CDC42) regulate actin reorganization, affecting diverse cellular responses, including adhesion, cytokinesis, and motility. Another major function of the Rho GTPases is their role in regulating transcriptional factors and nuclear signaling. RhoH is encoded by a hematopoiesis-specific Rho-related gene recently identified in a fusion transcript with bcl6 in lymphoma cell lines. Significantly, translocations and a high frequency of RhoH mutation have been detected in primary lymphoma cells. We show here that RhoH functions differently from other Rho GTPases. RhoH exerts no significant effect on actin reorganization. However, RhoH is a potent inhibitor of the activation of NFkappaB and p38 by other Rho GTPases. This property, together with the differential expression of RhoH in the Th1 subset of T cells, suggests a role for RhoH in the functional differentiation of T cells. RhoH has different amino acids in two highly conserved residues critical for GTPase activity. Consequently, RhoH is GTPase deficient, remaining in a GTP-bound activated state without cycling. Reduction of RhoH levels in T cells augments the response to Rac activation. Furthermore, RhoH is dramatically down regulated after phorbol myristate acetate treatment and in Th1 cells after activation by anti-CD3. Hence, a mechanism for regulation of RhoH function is likely to exist at the transcriptional level. The inhibitory function of RhoH supports a model in which Rho GTPases with opposing functions may compete to modulate the final outcome of a particular GTPase-activated pathway.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Activation of STAT transcription factors by the Rho-family GTPases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Oct 30;48(5):2213-2227. doi: 10.1042/BST20200468. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32915198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An essential role for Rac/Cdc42 GTPases in cerebellar granule neuron survival.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 19;276(42):39123-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103959200. Epub 2001 Aug 16. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11509562
-
Mechanisms of guanine nucleotide exchange and Rac-mediated signaling revealed by a dominant negative trio mutant.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 30;279(5):3777-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308282200. Epub 2003 Nov 3. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14597635
-
Rac1 and RhoG promote cell survival by the activation of PI3K and Akt, independently of their ability to stimulate JNK and NF-kappaB.Oncogene. 2002 Jan 10;21(2):207-16. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205036. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 11803464
-
Hematopoietic-specific Rho GTPases Rac2 and RhoH and human blood disorders.Exp Cell Res. 2013 Sep 10;319(15):2375-83. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23850828 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RhoH is critical for cell-microenvironment interactions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia in mice and humans.Blood. 2012 May 17;119(20):4708-18. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-395939. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22474251 Free PMC article.
-
Rho GTPases in kidney physiology and diseases.Small GTPases. 2022 Jan;13(1):141-161. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2021.1932402. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Small GTPases. 2022. PMID: 34138686 Free PMC article.
-
RhoE binds to ROCK I and inhibits downstream signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jun;23(12):4219-29. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.12.4219-4229.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12773565 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism-Based Redesign of GAP to Activate Oncogenic Ras.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Sep 20;145(37):20302-20310. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c04330. Epub 2023 Sep 8. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37682266 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of STAT transcription factors by the Rho-family GTPases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Oct 30;48(5):2213-2227. doi: 10.1042/BST20200468. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32915198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adamson, P., C. J. Marshall, A. Hall, and P. A. Tilbrook. 1992. Posttranslational modifications of p21rho proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 267:20033-20038. - PubMed
-
- Bagrodia, S., and R. A. Cerione. 1999. Pak to the future. Trends Cell Biol. 9:350-355. - PubMed
-
- Baldi, L., K. Brown, G. Franzoso, and U. Siebenlist. 1996. Critical role for lysines 21 and 22 in signal-induced, ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 271:376-379. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, A. S., Jr. 1996. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:649-683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
