The three mouse actin-depolymerizing factor/cofilins evolved to fulfill cell-type-specific requirements for actin dynamics
- PMID: 11809832
- PMCID: PMC65081
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.01-07-0331
The three mouse actin-depolymerizing factor/cofilins evolved to fulfill cell-type-specific requirements for actin dynamics
Abstract
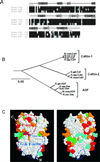
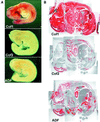
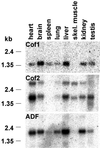
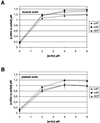
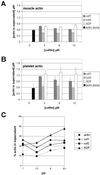
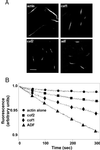
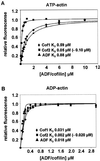
Actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF)/cofilins are essential regulators of actin filament turnover. Several ADF/cofilin isoforms are found in multicellular organisms, but their biological differences have remained unclear. Herein, we show that three ADF/cofilins exist in mouse and most likely in all other mammalian species. Northern blot and in situ hybridization analyses demonstrate that cofilin-1 is expressed in most cell types of embryos and adult mice. Cofilin-2 is expressed in muscle cells and ADF is restricted to epithelia and endothelia. Although the three mouse ADF/cofilins do not show actin isoform specificity, they all depolymerize platelet actin filaments more efficiently than muscle actin. Furthermore, these ADF/cofilins are biochemically different. The epithelial-specific ADF is the most efficient in turning over actin filaments and promotes a stronger pH-dependent actin filament disassembly than the two other isoforms. The muscle-specific cofilin-2 has a weaker actin filament depolymerization activity and displays a 5-10-fold higher affinity for ATP-actin monomers than cofilin-1 and ADF. In steady-state assays, cofilin-2 also promotes filament assembly rather than disassembly. Taken together, these data suggest that the three biochemically distinct mammalian ADF/cofilin isoforms evolved to fulfill specific requirements for actin filament dynamics in different cell types.
Figures

References
-
- Abe H, Endo T, Yamamoto K, Obinata T. Sequence of cDNAs encoding actin depolymerizing factor and cofilin of embryonic chicken skeletal muscle: two functionally distinct actin-regulatory proteins exhibit high structural homology. Biochemistry. 1990;29:7420–7425. - PubMed
-
- Adams ME, Minamide LS, Duester G, Bamburg JR. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a cDNA encoding chick brain actin depolymerizing factor. Biochemistry. 1990;29:7414–7420. - PubMed
-
- Ayscough KR. In vivo functions of actin-binding proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10:102–111. - PubMed
-
- Bamburg JR. Proteins of the ADF/cofilin family: essential regulators of actin dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1999;15:185–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

