Retinoic acid receptor alpha1 variants, RARalpha1DeltaB and RARalpha1DeltaBC, define a new class of nuclear receptor isoforms
- PMID: 11812818
- PMCID: PMC97588
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.24.4901
Retinoic acid receptor alpha1 variants, RARalpha1DeltaB and RARalpha1DeltaBC, define a new class of nuclear receptor isoforms
Abstract
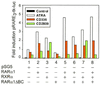
Retinoic acid (RA) binds and activates retinoid X receptor (RXR)/retinoic acid receptor (RAR) heterodimers, which regulate the transcription of genes that have retinoic acid response elements (RARE). The RAR isotypes (alpha, beta and gamma) are comprised of six regions designated A-F. Two isoforms of RARalpha, 1 and 2, have been identified in humans, which have different A regions generated by differential promoter usage and alternative splicing. We have isolated two new splice variants of RARalpha1 from human B lymphocytes. In one of these variants, exon 2 is juxtaposed to exon 5, resulting in an altered reading frame and a stop codon. This variant, designated RARalpha1DeltaB, does not code for a functional receptor. In the second variant, exon 2 is juxtaposed to exon 6, maintaining the reading frame. This isoform, designated RARalpha1DeltaBC, retains most of the functional domains of RARalpha1, but omits the transactivation domain AF-1 and the DNA-binding domain. Consequently, it does not bind nor transactivate RARE on its own. Nevertheless, RARalpha1DeltaBC interacts with RXRalpha and, as an RXRalpha/RARalpha1DeltaBC heterodimer, transactivates the DR5 RARE upon all-trans-RA binding. The use of RAR- and RXR-specific ligands shows that, whereas transactivation of the DR5 RARE through the RXRalpha/RARalpha1 heterodimer is mediated only by RAR ligands, transactivation through the RXRalpha/RARalpha1DeltaBC heterodimer is mediated by RAR and RXR ligands. Whilst RARalpha1 has a broad tissue distribution, RARalpha1DeltaBC has a more heterogeneous distribution, but with significant expression in myeloid cells. RARalpha1DeltaBC is an infrequent example of a functional nuclear receptor which deletes the DNA-binding domain.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Distinct binding determinants for 9-cis retinoic acid are located within AF-2 of retinoic acid receptor alpha.Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2323-30. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2323-2330.1994. Mol Cell Biol. 1994. PMID: 8139538 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of proteins that interact specifically with the retinoid X receptor: two novel orphan receptors.Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Jan;9(1):72-85. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.1.7760852. Mol Endocrinol. 1995. PMID: 7760852
-
Expression of retinoid X receptors and COUP-TFI in a human salivary gland adenocarcinoma cell line.Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;75(6):749-58. Biochem Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9599664
-
Nuclear retinoic acid receptor beta as a tool in chemoprevention trials.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(29):3553-63. doi: 10.2174/092986706779026183. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 17168722 Review.
-
Retinoic acid receptors at 35 years.J Mol Endocrinol. 2022 Oct 11;69(4):T13-T24. doi: 10.1530/JME-22-0097. Print 2022 Nov 1. J Mol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36149754 Review.
Cited by
-
[Research advances in the protective effect of all-trans retinoic acid against podocyte injury].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Jun;19(6):719-723. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2017.06.020. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28606243 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Role of retinoids in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015 Oct 15;7(10):184-203. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v7.i10.184. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26483874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting APP secretases: an overview on the holistic effects of retinoic acid receptor stimulation in APP processing.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jan 28;79(2):101. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04090-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35089425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Massive Effect on LncRNAs in Human Monocytes During Fungal and Bacterial Infections and in Response to Vitamins A and D.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 17;7:40598. doi: 10.1038/srep40598. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28094339 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Retinoic Acid Receptor (RAR) α Protein in the Synovial Membrane from Patients with Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Biomed Sci. 2007 Mar;3(1):46-9. Int J Biomed Sci. 2007. PMID: 23675020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wendling O., Ghyselinck,N.B., Chambon,P. and Mark,M. (2001) Roles of retinoic acid receptors in early embryonic morphogenesis and hindbrain patterning. Development, 128, 2031–2038. - PubMed
-
- Petkovich M., Brand,N.J., Krust,A. and Chambon,P. (1987) A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature, 330, 444–450. - PubMed
-
- Leid M., Kastner,P., Lyons,R., Nakshatri,H., Saunders,M., Zacharewski,T., Chen,J.Y., Staub,A., Garnier,J.M., Mader,S. and Chambon,P. (1992) Purification, cloning and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell, 68, 377–395. - PubMed
-
- Heyman R.A., Mangelsdorf,D.J., Dyck,J.A., Stein,R.B., Eichele,G., Evans,R.M. and Thaller,C. (1992) 9-cis Retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell, 68, 397–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

