Transcription factor Sp3 is regulated by acetylation
- PMID: 11812829
- PMCID: PMC97549
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.24.4994
Transcription factor Sp3 is regulated by acetylation
Abstract
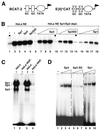
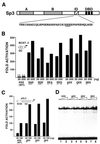
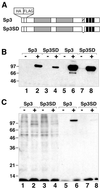
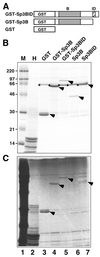
Sp3 is a ubiquitous transcription factor closely related to Sp1. Previous analyses showed that, unlike Sp1, Sp3 fails to activate transcription in certain promoter settings. This is due to the presence of an inhibitory domain located between the second glutamine-rich activation domain and the DNA-binding domain. To further analyze the transcriptional properties of Sp3, we have expressed and purified recombinant Sp3 and Sp1 as epitope-tagged proteins from stable transfected insect cells. We found that Sp3 does act as a strong activator similar to Sp1 in an in vitro transcription assay using Sp1/Sp3-depleted HeLa nuclear extract. However, on the same promoter Sp3 is almost inactive when transfected into cells. Mutational studies demonstrate that a single lysine residue is responsible for the low transcriptional activity of Sp3 in vivo. We show that Sp3, but not a mutant of Sp3 that lacks this lysine residue, is highly acetylated in vivo. Our results strongly suggest that the transcriptional activity of Sp3 is regulated by acetylation. The consequences of acetylation for the activity of Sp3 are discussed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An inhibitor domain in Sp3 regulates its glutamine-rich activation domains.EMBO J. 1996 Oct 15;15(20):5659-67. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8896459 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the promoter of human transcription factor Sp3 and evidence of the role of factors Sp1 and Sp3 in the expression of Sp3 protein.Gene. 2005 May 23;351:51-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.02.007. Epub 2005 Apr 25. Gene. 2005. PMID: 15857802
-
Estrogen regulation of trefoil factor 1 expression by estrogen receptor alpha and Sp proteins.Exp Cell Res. 2005 Jan 1;302(1):96-107. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.015. Exp Cell Res. 2005. PMID: 15541729
-
Interleukin-6 induces transcriptional activation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in astrocytes in vivo and regulates VEGF promoter activity in glioblastoma cells via direct interaction between STAT3 and Sp1.Int J Cancer. 2005 Jun 10;115(2):202-13. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20871. Int J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15688401
-
Sp1 control of gene expression in myeloid cells.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2004;14(3):171-81. doi: 10.1615/critreveukaryotgeneexpr.v14.i3.20. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2004. PMID: 15248814 Review.
Cited by
-
Lysine Acetylation Goes Global: From Epigenetics to Metabolism and Therapeutics.Chem Rev. 2018 Feb 14;118(3):1216-1252. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00181. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptotic sensitivity of colon cancer cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors is mediated by an Sp1/Sp3-activated transcriptional program involving immediate-early gene induction.Cancer Res. 2010 Jan 15;70(2):609-20. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2327. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20068171 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors stimulate mitochondrial HMG-CoA synthase gene expression via a promoter proximal Sp1 site.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Mar 15;31(6):1693-703. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg262. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12626711 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor suppressor p53 and histone deacetylase 1 are antagonistic regulators of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21/WAF1/CIP1 gene.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Apr;23(8):2669-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.8.2669-2679.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12665570 Free PMC article.
-
An acetylation/deacetylation-SUMOylation switch through a phylogenetically conserved psiKXEP motif in the tumor suppressor HIC1 regulates transcriptional repression activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Apr;27(7):2661-75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01098-06. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17283066 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

