Distribution of substitution rates and location of insertion sites in the tertiary structure of ribosomal RNA
- PMID: 11812832
- PMCID: PMC97625
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.24.5017
Distribution of substitution rates and location of insertion sites in the tertiary structure of ribosomal RNA
Abstract
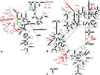
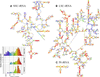
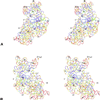
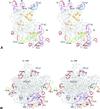
The relative substitution rate of each nucleotide site in bacterial small subunit rRNA, large subunit rRNA and 5S rRNA was calculated from sequence alignments for each molecule. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional variability maps of the rRNAs were obtained by plotting the substitution rates on secondary structure models and on the tertiary structure of the rRNAs available from X-ray diffraction results. This showed that the substitution rates are generally low near the centre of the ribosome, where the nucleotides essential for its function are situated, and that they increase towards the surface. An inventory was made of insertions characteristic of the Archaea, Bacteria and Eucarya domains, and for additional insertions present in specific eukaryotic taxa. All these insertions occur at the ribosome surface. The taxon-specific insertions seem to arise randomly in the eukaryotic evolutionary tree, without any phylogenetic relatedness between the taxa possessing them.
Figures


References
-
- Wimberly B.T., Brodersen,D.E., Clemons,W.M., Morgan-Warren,R.J., Carter,A.P., Vonrhein,C., Hartsch,T. and Ramakrishnan,V. (2000) Structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Nature, 407, 327–339. - PubMed
-
- Ban N., Nissen,P., Hansen,J., Moore,P.B. and Steitz,T.A. (2000) The complete atomic structure of the large ribosomal subunit at 2.4 Å resolution. Science, 289, 905–920. - PubMed
-
- Yusupov M.M., Yusupova,G.Zh., Baucom,A., Lieberman,K., Earnest,T.N., Cate,J.H.D. and Noller,H.F. (2001) Crystal structure of the ribosome at 5.5 Å resolution. Science, 292, 883–896. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz R.M. and Dayhoff,M.O. (1978) Ribosomal and other RNAs. In Dayhoff,M.O. (ed.), Atlas of Protein Sequence. National Biomedical Research Foundation, Silver Spring, MD, Vol. 5, supplement 3, pp. 327–337.

