Cytochrome c release from mitochondria proceeds by a two-step process
- PMID: 11818574
- PMCID: PMC122177
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.241655498
Cytochrome c release from mitochondria proceeds by a two-step process
Abstract
Cytochrome c is often released from mitochondria during the early stages of apoptosis, although the precise mechanisms regulating this event remain unclear. In this study, with isolated liver mitochondria, we demonstrate that cytochrome c release requires a two-step process. Because cytochrome c is present as loosely and tightly bound pools attached to the inner membrane by its association with cardiolipin, this interaction must first be disrupted to generate a soluble pool of this protein. Specifically, solubilization of cytochrome c involves a breaching of the electrostatic and/or hydrophobic affiliations that this protein usually maintains with cardiolipin. Once cytochrome c is solubilized, permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane by Bax is sufficient to allow the extrusion of this protein into the extramitochondrial environment. Neither disrupting the interaction of cytochrome c with cardiolipin, nor permeabilizing the outer membrane with Bax, alone, is sufficient to trigger this protein's release. This mechanism also extends to conditions of mitochondrial permeability transition insofar as cytochrome c release is significantly depressed when the electrostatic interaction between cytochrome c and cardiolipin remains intact. Our results indicate that the release of cytochrome c involves a distinct two-step process that is undermined when either step is compromised.
Figures
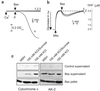
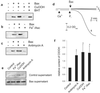
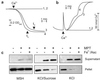
References
-
- Loeffler M, Kroemer G. Exp Cell Res. 2000;255:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Köhler C, Gahm A, Noma T, Nakazawa A, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B. FEBS Lett. 1999;447:10–12. - PubMed
-
- Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L, Wang X. Cell. 2000;102:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Verhagen A M, Ekert P G, Pakusch M, Silke J, Connolly L M, Reid G E, Moritz R L, Simpson R J, Vaux DL. Cell. 2000;102:43–53. - PubMed
-
- Li P, Nijhawan D, Budijardjo I, Srinivasula S M, Ahmad M, Alnemri E S, Wang X. Cell. 1997;91:479–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

