Experimental study on mechanism and protection of stress ulcer produced by explosive noise
- PMID: 11819360
- PMCID: PMC4723443
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v4.i6.519
Experimental study on mechanism and protection of stress ulcer produced by explosive noise
Abstract
AIM:To establish an experimental model of stress ulcer produced by explosive noise, and to probe into its mechanism and protection.METHODS:The country standard Wistar white rats were randomly divided into control group(n =8), which were neither stimulated nor protected, and stimulating group (divided into subgroups A, B and C, including 8 rats each which were decapitated to draw blood for test immediately, 12 hours and 24 hours after stimulation) and prevention group (divided into subgroups A, B and C, having 8 rats each, subgroup A was given cimetidine, B anisodamine and C both drugs). Firing noises of submachine guns were used as inflicting factor. The rats were fasted for 24 hours and stimulated by firing noise for 12 hours. The change of ulcer index, gastric mucosal and related serum hormones were observed.RESULTS:Stress ulcer was significant in the stimulating group, and its ulcer index (8.6 ± 0.6) was remarkably higher than that in both the control group and prevention group (0.3 ± 0.1, P < 0.01).Its serum gastrin (Gas ng/L, 294 ± 163 vs 63 ± 40,P< 0.01) and endothelin (ET ng/L, 181 ± 57 vs 135 ± 42, P < 0.1) were apparently higher than those in the control group, and its serum nitric oxide (NO) level was conspicuously lower than that in the control group (ng/L, 0.3 ± 0.1 vs 0.8 ± 0.5 P <0.5), while the serum gastrin level (ng/L, 556 ± 225) in prevention group was distinctly higher than that in both the control (P<0.1) and stimulating group (P < 0.5). There were no significant differences in the changes of ET and NO between the control and the stimulating groups.CONCLUSION:Stress ulcer model of rats can be successfully established by the stimulation of explosive noise. Gas, ET and NO are related to the formation of stress ulcer, and play an important role in its mechanism. Hepatic function affected by noise is observed in this experiment.
Figures
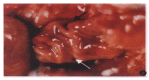
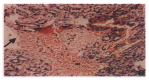
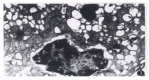

Similar articles
-
[Changes of rat gastric mucosal barrier under stress conditions].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2002 Jun;41(6):374-7. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 12137597 Chinese.
-
[Protection of gastric mucosa against steroids-induced damage by teprenone].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Oct 19;85(39):2749-53. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16324314 Chinese.
-
[A comparison study of post-cerebral hemorrhage stress ulcer with two interventional treatments aimed at endogenous endothelin in rat].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2008 Nov;20(11):678-80. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2008. PMID: 19000428 Chinese.
-
[Plasma polypeptide hormone levels in rats with gastric ulcer after exposure to intense noise].Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2003 Feb;21(1):48-50. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14761574 Chinese.
-
Effects and mechanism of changes of local neurotransmitters in rats' pylorus and bile reflux to the stomach with stress ulcer.Dig Dis Sci. 2005 Oct;50(10):1898-903. doi: 10.1007/s10620-005-2958-1. Dig Dis Sci. 2005. PMID: 16187194
Cited by
-
Anatomic and technical skill factor of gastroduodenal complication in post-transarterial embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 280 cases.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Mar 14;11(10):1554-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1554. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15770737 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota, Its Role in Induction of Alzheimer's Disease Pathology, and Possible Therapeutic Interventions: Special Focus on Anthocyanins.Cells. 2020 Apr 1;9(4):853. doi: 10.3390/cells9040853. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32244729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep deprivation increase the expression of inducible heat shock protein 70 in rat gastric mucosa.World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Aug;7(4):496-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i4.496. World J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11819816 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Psychological, Environmental and Physical Stressors on the Gut Microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2018 Sep 11;9:2013. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02013. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30258412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of occupational exposures and work characteristics with the occurrence of gastrointestinal disorders.Hippokratia. 2017 Apr-Jun;21(2):74-79. Hippokratia. 2017. PMID: 30455559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang XY, Zhang NZ. Modern field of internal medicine (in Chinese) Beijing: People's Military Medicine Publishing House. 1997:249–251.
-
- Guth PH, Aures D, Paulsen G. Topical aspirin plus HCl gastric lesions in the rat. Cytoprotective effect of prostaglandin, cimetidine, and probanthine. Gastroenterology. 1979;76:88–93. - PubMed
-
- Wan JL. Mechanism of formation of stress ulcer (in Chinese) Chin J Pathophysiol. 1993;9(5):664–666.
-
- Huang XQ, Wang YZ. Damage of noise to body and mind of patient (in Chinese) Med Information. 1995;8(6):279–280.
-
- Shi XY. Medical experimental zoology (in Chinese) Xi'an: Shaanxi Sci. & Tech Pub House. 1989;(6):56–62.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

