Liver biopsy:complications and risk factors
- PMID: 11819452
- PMCID: PMC4695539
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v5.i4.301
Liver biopsy:complications and risk factors
Abstract
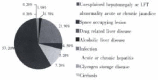
AIM:To study the complications and the risk factors of percutaneous liver biopsy, and to compare the complication rate between the periods of 1987-1993 and 1994-1996.METHODS:Medical records of all patients undergoing percutaneous liver biopsy between January 1, 1987 to September 31, 1996 in Songklanagarind Hospital were reviewed retrospectively.RESULTS:There were 484 percutaneous liver biopsies performed. The total complication rate was 6.4%, of which 4.5% were due to major bleeding; the death rate was 1.6%. The important risk factors correlated with bleeding complications and deaths were a platelet count of 70X10(9)/L or less, a prolonged prothrombin time of >3seconds over control, or a prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time of > 10 seconds over control. Although physician inexperience was not statistically significantly associated with bleeding complications and deaths, there was a reduction of death rate from 2.2% in 1987-1993 to 0% in 1993-1996. This reduction is thought to result from both increased experience of senior staff and increased supervision of residents.CONCLUSIONS:Screening of platelet count, prothrombin time, and activated partial thromboplastin time should be done and need to be corrected in case of abnormality before liver biopsy. Percutaneous liver biopsy should be performed or supervised by an expert in gastrointestinal diseases, especially in high risk cases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bleeding time in patients with hepatic cirrhosis.BMJ. 1990 Jul 7;301(6742):12-5. doi: 10.1136/bmj.301.6742.12. BMJ. 1990. PMID: 2383699 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of bleeding risk in percutaneous renal biopsy in Tibet].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021 Mar 11;53(2):298-301. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2021.02.011. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021. PMID: 33879901 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Predictors of bleeding complications in percutaneous ultrasound-guided renal biopsy.Kidney Int. 2004 Oct;66(4):1570-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00922.x. Kidney Int. 2004. PMID: 15458453
-
Transjugular biopsy of the liver.Clin Gastroenterol. 1985 Apr;14(2):451-67. Clin Gastroenterol. 1985. PMID: 4028481
-
Bleeding complications after transcutaneous kidney biopsy in patients with systemic amyloidosis: single-center experience in 101 patients.Am J Kidney Dis. 2008 Dec;52(6):1079-83. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.05.022. Epub 2008 Jul 23. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008. PMID: 18649980
Cited by
-
Osteopontin contributes to TGF-β1 mediated hepatic stellate cell activation.Dig Dis Sci. 2012 Nov;57(11):2883-91. doi: 10.1007/s10620-012-2248-7. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Dig Dis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22661273
-
Concordance of Solid Organ Biopsy Diagnoses With Hospital Autopsy and the Contribution of Biopsies to Death.Cureus. 2023 Jan 17;15(1):e33889. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33889. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36819431 Free PMC article.
-
Complication rate of percutaneous liver biopsies among persons with advanced chronic liver disease in the HALT-C trial.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Oct;8(10):877-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.03.025. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 20362695 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Narrative review of vascular iatrogenic trauma and endovascular treatment.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jul;9(14):1199. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4332. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34430640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Checkmate to liver biopsy in chronic hepatitis C?World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Oct 21;18(39):5514-20. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5514. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23112543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherlock S. Diseases of the liver and biliary system: needle biopsy of the liver. 8th ed. Boston, Melbourne: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1989. pp. 36–48.
-
- Valori R, Elias E. How to perform a percutaneous liver biopsy. Br J Hosp Med. 1989;42:408–410. - PubMed
-
- Stotland BR, Lichtenstein GR. Liver biopsy complications and routine ultrasound. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:1295–1296. - PubMed
-
- McGill DB. Predicting hemorrhage after liver biopsy. DigDis Sci. 1981;26:235–237.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources