Effect of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion on expressions of endogenous basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor betain lung and its relation with lung repair
- PMID: 11819596
- PMCID: PMC4688750
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i3.353
Effect of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion on expressions of endogenous basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor betain lung and its relation with lung repair
Abstract
AIM:To study the changes of endogenous transforming growth factor beta(TGFbeta) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in lung following intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury and their effects on lung injury and repair.METHODS:Sixty Wistar rats were divided into five groups, which underwent sham-operation, ischemia (45 minutes), and reperfusion (6, 24 and 48 hours, respectively) after ischemia (45 minutes). Immunohistochemical method was used to observe the localization and amounts of both growth factors.RESULTS:Positive signals of both growth factors could be found in normal lung, mainly in alveolar cells and endothelial cells of vein. After ischemia and reperfusion insult, expressions of both growth factors were increased and their amounts at 6 hours were larger than those of normal control or of 24 and 48 hours after insult.CONCLUSION:The endogenous bFGF and TGF beta expression appears to be upregulated in the lung following intestinal ischemia and reperfusion, suggesting that both growth factors may be involved in the process of lung injury and repair.
Figures
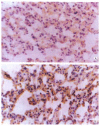
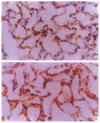
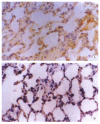
References
-
- Fu XB. Treatment of internal organ damage by growth factors. Xin Xiaohuabingxue Zazhi. 1997;5:663–664.
-
- Yang YH, Fu XB, Sun TZ, Wang YP, Sheng ZY. bFGF and TGF-β gene expression inrat lung after ischemia reperfusion. Jiefangjun Yixue Zazhi. 1998;23:405–409.
-
- Guan J, Jin DD, Jin LJ. [JP2] Apoptosis in rat lung after shock caused by multiple injuries. Zhongguo Weizhongbing Jijiu Yixue. 1998;10:479–483.
-
- Turnage RH, Guice KS, Oldham KT. Endotoxemia and remote organ injury following intestinal reperfusion. J Surg Res. 1994;56:571–578. - PubMed
-
- Turnage RH, Kadesky KM, Bartula L, Myers SI. Intestinal reperfusion up-regulates inducible nitric oxide synthase activity within the lung. Surgery. 1995;118:288–293. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

