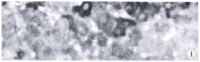
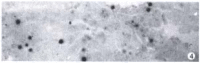
Kupffer cell and apoptosis in experimental HCC
- PMID: 11819610
- PMCID: PMC4688764
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i3.405
Kupffer cell and apoptosis in experimental HCC
Figures
References
-
- Zhu H, Ruan Y, Wu Z. [The influence of Kupffer cells on experimental hepatocarcinogenesis] Zhonghua Binglixue Zazhi. 1998;27:102–104. - PubMed
-
- Kukan M, Vajdová K, Horecký J, Nagyová A, Mehendale HM, Trnovec T. Effects of blockade of Kupffer cells by gadolinium chloride on hepatobiliary function in cold ischemia-reperfusion injury of rat liver. Hepatology. 1997;26:1250–1257. - PubMed
-
- Decker K. Biologically active products of stimulated liver macrophages (Kupffer cells) Eur J Biochem. 1990;192:245–261. - PubMed
-
- Hung WC, Chuang LY. Induction of apoptosis by sphingosine-1-phosphate in human hepatoma cells is associated with enhanced expression of bax gene product. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;229:11–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources