Effect of hepatocyte apoptosis induced by TNF-alpha on acute severe hepatitis in mouse models
- PMID: 11819675
- PMCID: PMC4688844
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i5.688
Effect of hepatocyte apoptosis induced by TNF-alpha on acute severe hepatitis in mouse models
Abstract
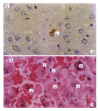
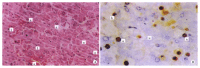
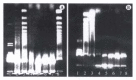
AIM:To study the effect of hepatocyte apoptosis and necrosis induced by TNF-alpha on the pathogenesis of acute severe hepatitis (ASH).METHODS:The model of ASH was prepared in D-galactosamine (GalN) sensitized BALB/c mice by injection of either endotoxin (ET) or tumor necrosis factor-alpha(TNF-alpha. Morphological changes of apoptotic hepatocytes were studied by both light and electron microscope and in site end labeling method (ISEL). Molecular biological changes of DNA ladder were observed by electrophoresis of extract from liver tissues. Biochemical changes were measured by alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartic aminotransferase (AST) and TNF-alpha. The relation between apoptosis and necrosis was evaluated simultaneously.RESULTS:The sequence of hepatocyte apoptosis, necrosis, and final death from ASH was observed both in GalN/ET and GalN/TNF-alpha group. Apoptosis was prominent at 3.5h and 6h after injection of inducer, while necrosis became dominant at 9h after challenge. The appearance of apoptosis was earlier in GalN/TNF-alpha group than that in GalN/ET group. Pretreatment of mice with antiTNF IgG1 may completely prevent the liver injury induced by GalN/ET.CONCLUSION:TNF-alpha can cause liver amage by inducing hepatic apoptosis and necrosis in mice with endotoxemia.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanism for hepato-protective action of Liangxue Huayu Recipe (LHR): blockade of mitochondrial cytochrome c release and caspase activation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jul 30;148(3):851-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.024. Epub 2013 May 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23711831
-
Caspase activation during hepatocyte apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha in galactosamine-sensitized mice.Liver. 2001 Oct;21(5):309-19. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0676.2001.210503.x. Liver. 2001. PMID: 11589767
-
N-acetylcysteine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptotic liver damage in D-galactosamine-sensitized mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007 Nov;28(11):1803-9. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007. PMID: 17959032
-
Etoposide prevents apoptosis in mouse liver with D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced fulminant hepatic failure resulting in reduction of lethality.Hepatology. 2001 Jun;33(6):1441-50. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.24561. Hepatology. 2001. PMID: 11391533
-
Lethal hepatic apoptosis mediated by tumor necrosis factor receptor, unlike Fas-mediated apoptosis, requires hepatocyte sensitization in mice.J Hepatol. 1999 Dec;31(6):997-1005. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80311-0. J Hepatol. 1999. PMID: 10604572
Cited by
-
Pharmacology of tetrandrine and its therapeutic use in digestive diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Oct;7(5):627-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i5.627. World J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11819843 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Impact of the Gut Microbiome on the Progression of Hepatitis B Virus Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Apr 6;11:573923. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.573923. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33889550 Free PMC article.
-
Neutron-induced apoptosis of HR8348 cells in vitro.World J Gastroenterol. 2001 Jun;7(3):435-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i3.435. World J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11819807 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The analysis of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase gene in different type liver tissues.World J Gastroenterol. 2003 Feb;9(2):276-80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i2.276. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12532447 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody prevents brain damage of rats with acute necrotizing pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Oct 1;10(19):2898-900. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i19.2898. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15334696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ogasawara J, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Adachi M, Matsuzawa A, Kasugai T, Kitamura Y, Itoh N, Suda T, Nagata S. Lethal effect of the anti-Fas antibody in mice. Nature. 1993;364:806–809. - PubMed
-
- Tagawa Y, Sekikawa K, Iwakura Y. Suppression of concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in IFN-gamma(-/-) mice, but not in TNF-alpha(-/-) mice: role for IFN-gamma in activating apoptosis of hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1997;159:1418–1428. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

